Programming or coding has been occupying the practical
world for a long period of time now. Our modern world offers a huge
opportunity for those with a computer science[1]
background. In fact, people from other sectors, as well, train
themselves additionally to enter this world of opportunity.
Hence, candidates expecting a decent job of programming
should definitely prepare themselves for the upcoming programming
interview questions. Here, every interview question requires a
smart answer to the board’s smart inquiry. Programming Interview
Questions usually include questions of three categories –
Data structure,
algorithms, and
logical questions as
well.
Your interview review board will not be complete unless
you have gone through these three types of question
categories.
Programming Interview Questions and
Answers
As said earlier, an interview board for programming or coding
based jobs will require knowledge over three types of question
categories. Here, we are going to cover those possible programming
interview questions. So, once you have gone through our collection
of questions, you should feel confident enough to face the
interview board.
1. What do you mean by “Computer
Programming”?
 This is one of the very basic programming
This is one of the very basic programming
interview questions. It is often asked at the beginning of every
interview. Our collection will include such common questions for
you to cover up all the levels of the interview.
Computer programming, also known as computer coding, is a series
of tasks implemented to achieve certain figurative results. The
process takes place through the meaningful execution of computer
programs. It involves planning and coding algorithms, reforming a
program, and also maintenance and updating different structured
codes.
Computer programming is executed by any of the programming
languages available. Every programming language is actually a group
of instructions that command the machine to execute any specific
task set by the programmer. Computer programming is a complex
process that requires knowledge over specific programming languages
users want to use to obtain the specific output.
2. Do you know about High level
and Low-level programming languages?
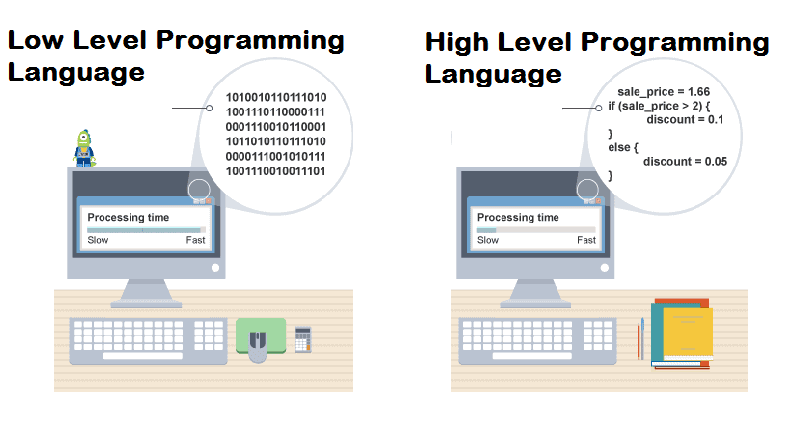 Yes, I can. High-level programming languages are not
Yes, I can. High-level programming languages are not
dependent on the machine type you are using. A high-level
programming language is highly simplified. It is close to regular
languages so that programmers can have an easy experience with
program development. For example, C, Java, FORTRAN, etc. are
high-level programming languages. [2]
On the contrary, low-level language is close to machine
language. The low-level programming language offers no
simplification of machine instructions. Such as Assembly
language.
3. What are “translators” in computer
programming?
Translators in computer programming are processors for different
programming languages. Translators convert programming languages
and make it readable by the machine. In a word, translators
translate different programming languages into machine languages.
There are three types of translators in computer programming. They
are,
Compiler & Interpreter: Compilers and
Interpreters are both alike. They both convert high-level
programming language into low-level programming languages. They
convert any programming language (such as C programming) into
machine language.
Assembler: Assembler in computer programming is
a program. It transforms assembly language into machine
language.
4. Can you explain what “debugging”
is?
 Debugging is a process. Through this process, your machine
Debugging is a process. Through this process, your machine
can find faults or errors in your programming. It also resolves or
fixes defects that prevent your written code from executing certain
tasks.
This process is continued through Debuggers[3], a software that helps
programmers to find errors, execute a program, monitor the entire
process, and stop it whenever it is needed.
5. What do you know about
“Variables”?

Constants and variables are very usual terms in computer
programming. The next following three questions in our list of
programming interview questions are based on constants and
variables.
Variables are often referred to as “containers” for information.
They reserve information that is to be mentioned in programming
later. Variables can also be modified for the proper execution of
code anytime, anywhere. Variables are separated by memory address,
a.k.a location. Often they come with symbolic addresses whose value
can be changed according to the requirement of programmers.
The main purpose of variables is to stock data. This data can be
used throughout your programming.
6. Please explain what “constant” is
and its types.
In computer programming, a constant is such a unit whose value
cannot be changed throughout the implementation of the programming.
There are two types of constants available in coding.
Numeric Constant: This type of constants are
numbers. Such as 5, 19, 33.1, etc. Integers, floats, single and
double precision numbers, etc.
String Constant or String Literals: String
constants, in programming, hold alphabetical characters. You can
hold sequential characters in a string constant as well. However,
whether it is a single character or sequential, it has to be placed
inside double-quotes. For example, “I am going for a trip” is a
string constant that holds 20 characters.
Note, you can place a maximum of 255 characters as a string
constant, including ‘space.’
7. What’s the difference between
variables and constants?
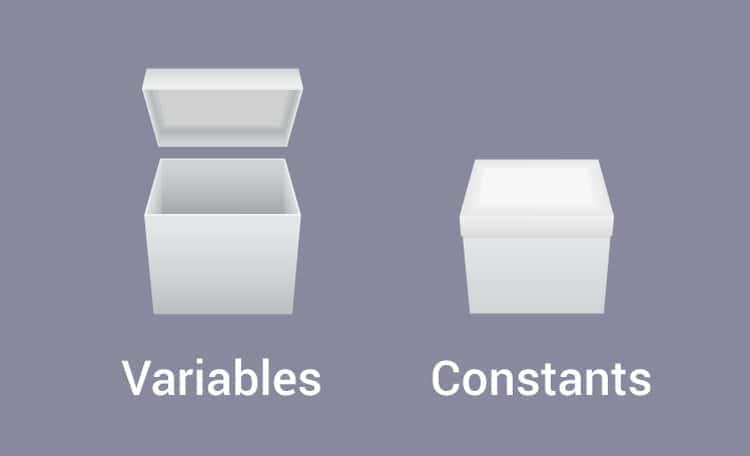 A constant
A constant
in programming is considered similar to variables. However,
constants cannot change its value. Once a constant has been
defined, it will be the same throughout the entire programming.
However, when it comes to variables, anytime the value of a
variable can be changed or set to a new one to influence the
output.
A constant, in computer programming, is a fixed value. Whereas,
a variable is a memory location. When you manipulate a variable,
the memory location remains the same; however, only the value, it’s
been holding changes.
8. Can you explain what an “algorithm”
is?
 In computer
In computer
programming, an algorithm is defined as a collection of limited
steps. It is also regarded as a computer procedure, a procedure
that commands your machine to take certain steps and execute
certain tasks. It actually comes in a step by step procedure. While
writing an algorithm, programmers should be aware of clarity, it’s
limit, and it’s productivity.
An algorithm is not only a series of steps. It can also
influence data in different ways. For example, through an
algorithm, you can place new data within the set of steps, follow a
repetitive command or search for a specific item.
9. Do you know about the
“flowchart”?
The flowchart in computer programming is a diagram that
represents programming algorithms. Each step of algorithms is shown
in sequential boxes that are connected by arrows. These arrows have
to be set in order. Otherwise, the goal of performing certain
logical tasks won’t be complete.
Note, the flowchart in programming comes in four general steps.
They are Start, Process, Decision, End.
10. What are “Keywords” in computer
programming?
Keywords in computer programming are reserved words. These
reserved words have special meaning for a specific programming
language. Keywords are used for serving specific purposes. One
particular keyword is not replaceable for another keyword. Every
programming language has a set of keywords. Also, keywords cannot
be used as variables or constants.
Some examples for keywords are break, if, for, char, else, float
for C Programming, continue, del, lambda, not, def
and others for Python, abstract, implements,
finally, double, volatile, and others for
Java.
11. What do you know about
“operators.”
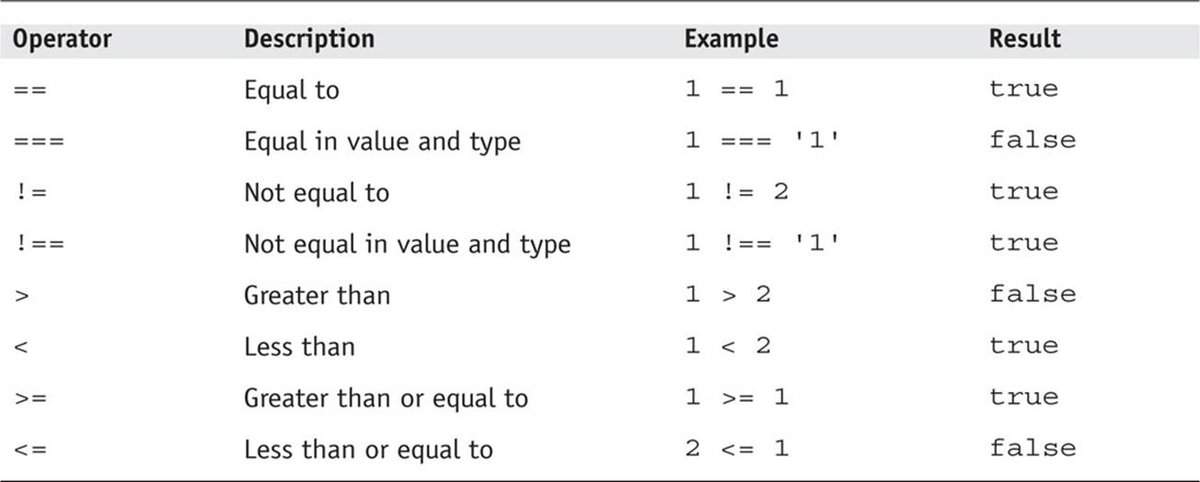
Operator is a mandatory term in programming. Whether it adds as
one of the programming interview questions or not, you should be
well aware of it.
Operators are special symbols in computer programming. They are
used for carrying out mathematical (also includes logical and
relational) operations in programming. It tells your compiler/
interpreter to perform specific mathematical tasks and bring the
output. For example, asterisk sign (*) represents mathematical
multiplication while double && represents logical and in
different programming languages.
There are four kinds of operators,
Arithmetic,
Assignment,
Logical, and
Relational.
Arithmetic operators stand for mathematical operators. It
includes “+” for addition, “-” for subtraction, “*” for
multiplication, “/” for the division.
Assignment operators are used to assigning different values or
new outputs and strings to variables.
Logical operators are used for decision making based on given
conditions. In other words, logical operators help your machine to
get to the final result based on several conditions starting from
simple to complex.
Relational operators allow you to justify any given relationship
between two units. They indicate whether true or false relations.
For example, greater than stands for (>), less than or equal to
stands for (≤).
12. Can you explain “reliability” in
the programming language?
Reliability, in computer programming, defines how better off or
crush-resistant your written codes are. A specific period of time
will be given. And if your codes work properly during this period
of time, it will be considered reliable. Otherwise, if the program
crashes, it will not be considered reliable.
Reliability doesn’t depend on which programming language you are
using to compose. But it does depend on how you have written your
code.
13. What is “modeling
language”?
The modeling language is any kind of graphical language in
computer programming. It is not entirely an artificial language
but, however, similar to one. Modeling language provides a proper
expression of a system, construction of a model, or information
through an organized set of rules and regulations.
Some examples of modeling languages are:
- Flowchart
- Express
- System modeling language.
- Jackson modeling language.
- Extended enterprise modeling language.
- Business processing modeling language.
- Unified modeling language.
14. Mention the errors that occur while
executing a program?

Errors in computer programming is a very common issue. We are
sure it will add to your list as one of the major programming
interview questions.
There are three types of errors that can interfere with the
execution of computer programming. They are:
- Runtime error.
- Logical error.
- Syntax error.
15. Explain different types of errors
in computer programming.
Let’s start with Runtime error,
Runtime Error: Runtime error takes place when a program is led
to illicit activity. Such as dividing an integer with zero.
Fortunately, when a runtime error happens, it is displayed
immediately by your computer. Your machine will stop the program
immediately and show an identifying message. Hence, you can easily
find out where the error occurred and fix it.
Logical Error: Logical errors are the hardest
errors to locate. It takes place when there is an incorrect logic
in the codes. As it is entirely upon the nature of the program,
your compiler or interpreter cannot detect this fault in the logic;
hence, these are very problematic to find out.
Syntax Error: There are
certain grammatical regulations in computer programming. A syntax
error occurs when there is a defiance of these rules. When your
program runs through compile-time, syntax error can be easily
detected on the exact line it has occurred.
16. Explain what “Maintain and update
the program” means.
Yes. Maintaining and updating the program is an after process to
make new modifications to an already delivered software or
hardware.
When you release new software or hardware, there can be bugs or
faults that are needed to be fixed. Hence, developers need to
modify core programming to eliminate the problem. Sometimes
updating programs can also come with increasing the performance of
software, adding a new feature, or bringing modification to the
existing ones.
17. Can you explain what “arrays”
are?
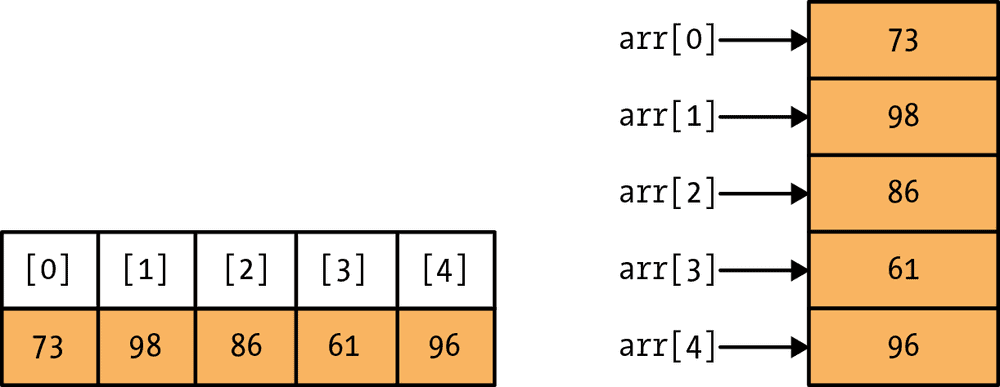
This is one of the very common programming interview questions.
More or less, every candidate has to face this question. Here is
what the answer is,
Arrays in computer programming are a type of data structure that
holds the same type of data in a group. Its main function is to
store data of the same type. However, you can also consider an
array as a set of variables of the same category. As variables are
memory locations. Hence, arrays can also be defined as a set of
memory locations as well.
For example, int stu[50]. Here, stu is an array that can store
up to 50 components that are of integer type. You can also define
an array without its dimension as well. However, in this case, you
have to mention the elements like this,
Int stu[ ] = (1, 2, 3 …… 50)
Arrays can also be of float and char type as well.
18. What is a multidimensional
array?
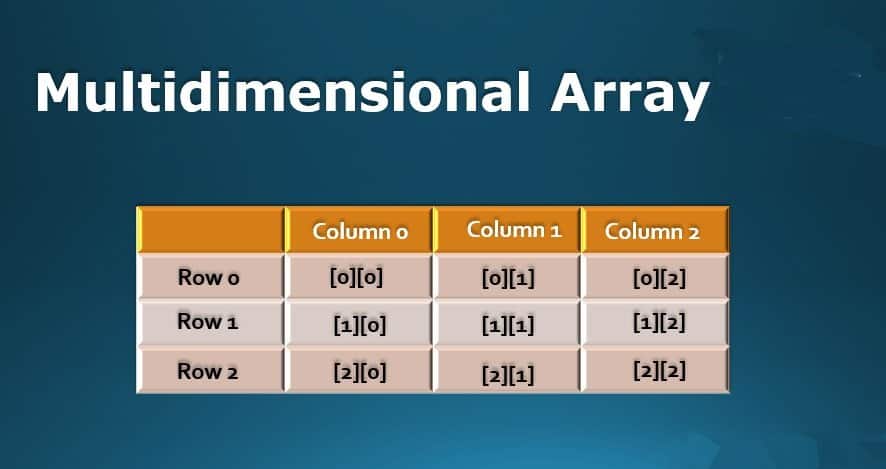 Any array in
Any array in
computer programming that holds more than one dimension is known as
a multidimensional array. In other words, it is an array that holds
other arrays or several indexes. In computer programming, a
single-dimensional array is easy to read and write. But, however,
it is not applicable to different aspects of a project. Hence, a
typical code work will need more than a one-dimensional array. This
is where multi-dimensional arrays are used.
The lowest levels of arrays that can be called a
multi-dimensional array is a 2D dimensional array.
19. Can you explain what “subroutine”
is?
 A subroutine is a series of instructions.
A subroutine is a series of instructions.
They hold instructions for computer programs. Subroutines are used
for carrying out particular tasks grouped as a unit. Based on
different programming languages[4], subroutines are known
by different names, such as functions, sub-programs, routines, or
procedures, and some other.
Note, Subroutines can be called from anywhere in
programming. Based on where you call them, they will perform that
specific task there.
20. What do you know about
“loops”?
 These types of questions are very common in the programming
These types of questions are very common in the programming
interview board. Every serious candidate should be aware of these
programming interview questions.
In coding, a loop is such an instruction that repeats itself
until a certain condition is met. In other words, a loop is a form
of instruction. More elaborately, every loop in programming holds
an inquiry. A loop runs several times until the inquiry is met.
There are three types of loops in computer programming.
For Loop: For loop is the most used loop in
programming. Here, programmers are aware of the loop number they
are about to set.
While Loop: This loop comes handy when the
programmer is not aware of the number of loops. While the loop
keeps on repeating until the given condition is not true
anymore.
Nested Loop: The Nested loop is different from the
For and While loop. When one loop is placed inside another one, it
is called a nested loop.
21. What is the machine code?
 Machine codes are also known as machine language. It is
Machine codes are also known as machine language. It is
considered the basic language of programming. Usually, other
programming languages are first interpreted by translators, and
they can be readable by the computer’s CPU. However, machine
language needs no such translators, and they can be directly
executed by your machine.
Machine language is actually written in binary numbers. Every
machine has its own particular machine language. They command the
CPU to execute certain tasks.
22. What is the “beta version” of a
program?
A beta version of a computer program indicates an initial
release of computer software, which is, however, not fully ready
yet. It will have feedback and fixes and then modified for the
final version.
It is a pre-release of the final version of the software. A big
number of users are the target audience of the beta software. They
will give full review and feedback for the improvement of the beta
version. The beta version of a software is similar to the actual
product in look and function as well.
23. What is the data
structure?
 A data structure is a particular process of managing
A data structure is a particular process of managing
data in a machine. In this process, data is maintained in such a
way that they can be used more proficiently later on a computer. It
is also known as data management, as well.
The data structure also refers to the storage of data values,
relations between them, and the operations that can be implemented
to them, through which efficient modification is done to the
collection of data. Some examples of data structures are arrays,
graphs, and stacks.
24. Please explain the linear and
non-linear data structures.
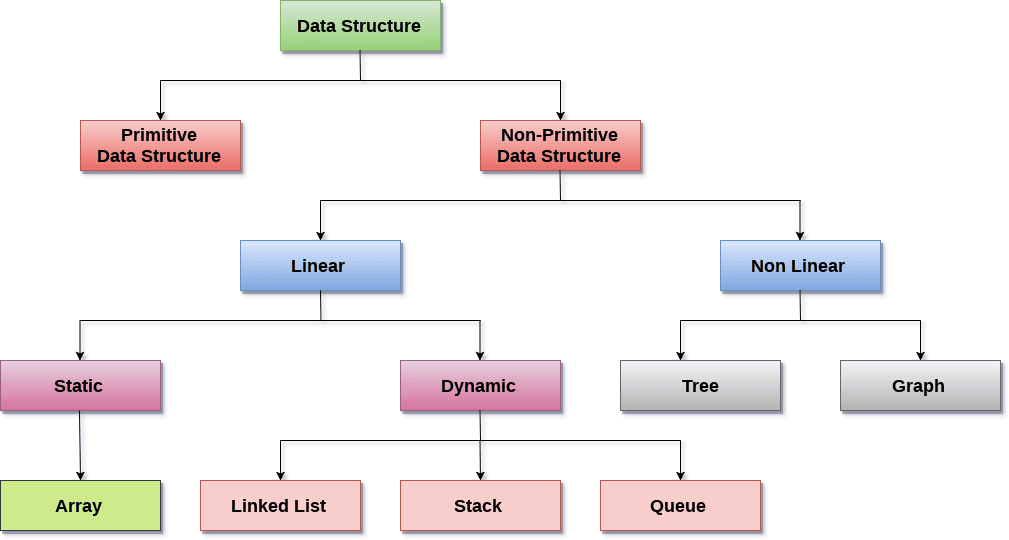 In a linear data structure, elements of the data structure
In a linear data structure, elements of the data structure
are organized in a linear sequence. Here, each data element of the
data structure establishes a connection with its previous and next
adjoining. In other words, every data element is placed between its
previous and next data elements. It is like a series of
connections. Some examples of the linear data structure are array,
stack, a list that is linked.
The non-linear data structure is, however, the exact opposite of
linear data. Here, data elements are connected at random. Here, one
data element can have a connection with several data elements (more
than two specifically). A non-linear data structure is more complex
than a linear data structure. Here, all the elements cannot be
moved in a single execution only. Some examples of non-linear data
structures are graphs, trees.
25. How does data structure help in
practical life?
The easy part is over with our list of programming interview
questions. With our next question, we are about to enter the
intermediate level of coding interview questions. Here is what the
answer should be,
The data structure is essential for areas where things are
mostly controlled through data. Every day in our day to day life,
we need things done through data. Hence, data structure plays a
vital role in different aspects of our life. Some noteworthy areas
where the data structure is mandatory are:
- Organizing database.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Numeric analysis.
- Different operational systems.
26. Can you explain what software
testing is?
Software testing is a very common term in the programming world.
And one of the very commonly asked programming interview
questions.
Software testing is a process of testing a newly developed
software under certain conditions. Software testing plays an
important role in the industry of software development. Every
software, whether it is a waterfall model or a RAD (Rapid
Application Development) model requires to go through this process
as the final preparation of software release. Software testing also
ensures whether software provides a better user experience or not.
Reasons why software testing is needed are:
- Makes sure the software works properly.
- Ensures quality.
- Checks whether the software meets user requirements or
not.
27. Do you know what analyzing a
program means?
 In the process of analyzing a program, developers divide the
In the process of analyzing a program, developers divide the
program into several sub-problems. In this way, programmers don’t
have to solve the large problem at once, rather solving the
sub-problems will do just fine. Then the total solutions of the
sub-problems will come together to provide the most reasonable
solution to the entire problem.
Note, analyzing a program is often referred to as the top-down
design initiative.
28. What do you know about implementing
a program?
When the process of software testing has been gone thoroughly,
the next step is the implementation of a program. Once a program is
thoroughly tested, it has to be installed on the end user’s device.
After proper installation, the program has to be put into
action.
This process of program installation and putting them into
operation to the targeted destination is known as program
implementation.
29. Please explain the program
execution.
A program can come with a large number of instructions. To
complete the specific task set in a program, your computer will
execute those instructions. This process is called the execution of
a program.
Note, before a proper execution of a program, it has to be
loaded into your computer memory (RAM).
30. Explain how debugging is related to
software testing.
 Software testing puts the software in the
Software testing puts the software in the
test under specific conditions. While debugging is the process of
finding faults in a program. In this process, debuggers (debugging
tools/ software) are used to find errors (bugs or issues) in a
program under different development stages. Those conditions in
which the problems have occurred are reproduced, and the program is
run over again to discover what caused the problem at first.
Note, debugging is an essential part of software testing. And
hence plays a great role in the software development industry.
31. What is documentation in computer
programming?
 Not every candidate is aware of
Not every candidate is aware of
documentation in programming. Hence, in case you don’t miss it, you
should focus on these kinds of programming interview questions as
well.
Documentation in computer programming is a written explanation
of the code techniques used in that program, and it’s layout, test,
and algorithm. It also holds the applications for specific computer
programs.
Documentation is important for those who run the program or the
program based application once in a while. It is also useful for
regular programmers who need to update, change, or edit any part of
the codes. Documentation helps to provide an easy solution related
to that specific program for all kinds of programmers.
 A regular computer program can hold up to
A regular computer program can hold up to
thousands of lines of code (LOC). It is not very unusual even for a
professional programmer to lose track of any single line of code.
Hence, comments can help us understand the significance of any
single line of code. Adding comments will make the user’s
experience easy with programming.
Comments are allowed in every programming language. Programmers
can add as much comment as they need. However, comments won’t
affect your program in any way.
33. Suggest some good practices in
computer programming.
Yes, certain practices in computer programming can help improve
your skills in programming. They are:
- Your program should follow the DRY theory.
- Maintain the simplicity of your code.
- Keep some common protocols for naming.
- Make sure you do not use too many nested loops.
- Maintain a proper length for your written codes.
- To avoid complexity, use comments more frequently.
34. What is the DRY Principle?
 DRY is also known as Do not Repeat Yourself is a software
DRY is also known as Do not Repeat Yourself is a software
development protocol. As the name suggests, the DRY principle in
software development helps users so that they don’t duplicate the
same software patterns in software.
In order to implement DRY policy, repetitive software patterns
are exchanged with abstractions. However, one can also employ a
data normalization process to avoid such situations.
35. Do you know about WET
solutions?
A few advanced levels of programming interview questions are
very common to face before the board. The answer is,
Yes, I do. The WET solution is exactly the opposite of a DRY
solution. You see, WET mostly means Write Everything Twice.
Although the term has several other abbreviations as well, such as:
“Write Every Time,” “We Enjoy Typing,” “Waste Everyone’s Time.”
Note, In application, WET solutions are noticeable in
multi-layered architecture where demonstration, process policy of
the application, and activities related to data management are
disconnected separately.
36. What do you know about LIFO and
FIFO?
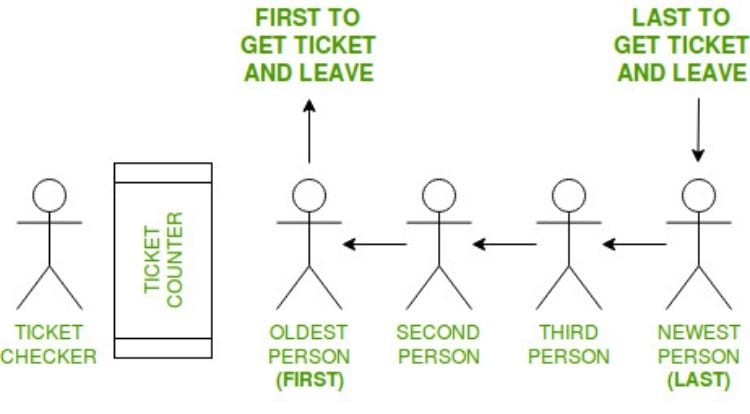 LIFO and FIFO are two popular approaches
LIFO and FIFO are two popular approaches
in computer programming. They are useful in the sense that, LIFO
and FIFO help to manage (data access, recover data, or storing
data) data structures in two different ways.
LIFO, as in Last In
First Out, is the policy where newly stored data
is processed first. LIFO is also known as FILO (First In, Last
Out). While processing data in the LIFO form, LIFO is
stack.
Whereas, FIFO stands for First
In First Out. In FIFO, the first element of data structure is
managed first, and the latest element is recovered at last. Unlike
LIFO, FIFO is queue during the implementation of data
structure.
37. What is NULL and VOID in
programming?
 Null in programming doesn’t really
Null in programming doesn’t really
indicate that the variable presents no value. Rather it means that
the variable contains no valid value. In programming, a variable
having a null value means that a variable with an empty value. Some
null values can be returned based on the essentials of a
program.
VOID value, on the other hand, represents no primary size. Void
values in a variable do not return at all.
38. What is an AVL tree?
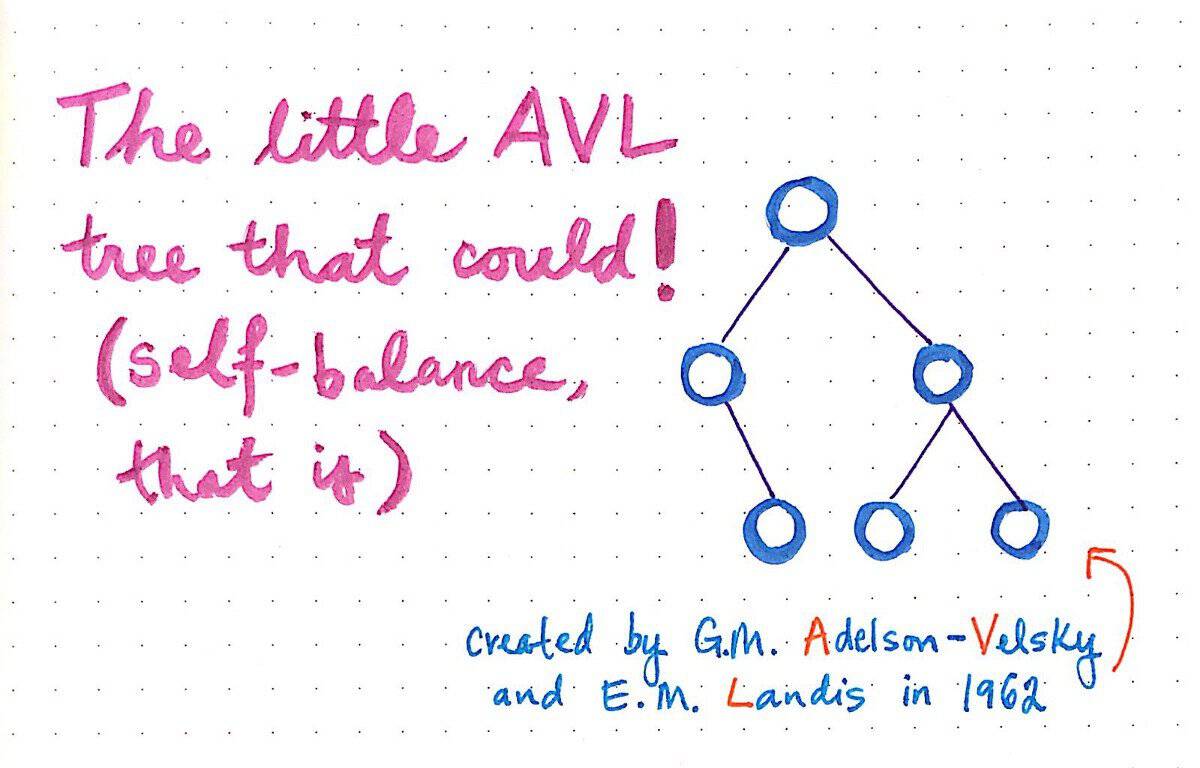 To win over the competition with other
To win over the competition with other
candidates, you should definitely be aware of the AVL tree. It is
one of the very regular programming interview questions.
In computer programming, an AVL tree is a partly balanced
binary search tree. In this form of data structure, there is a
limit set in the height between the right and left subtrees of a
node. The difference is 1 or less than 1 in every case. AVL tree is
the first of its kind.
However, if there is any imbalance found (subtrees height
difference becoming more than), rebalance will be done
immediately.
39. What is Sorting in Computer
Programming?
Sorting in computer programming is a method of organizing
elements of a data structure in an ascending (uprising) or
descending sequence. There are several types of sorting types
available in computer programming. They are:
- Bubble Sort.
- Selection Sort.
- Merge Sort.
- Heap Sort.
- Insertion Sort.
- Quick Sort.
40. Do you know about Bubble
Sorting?
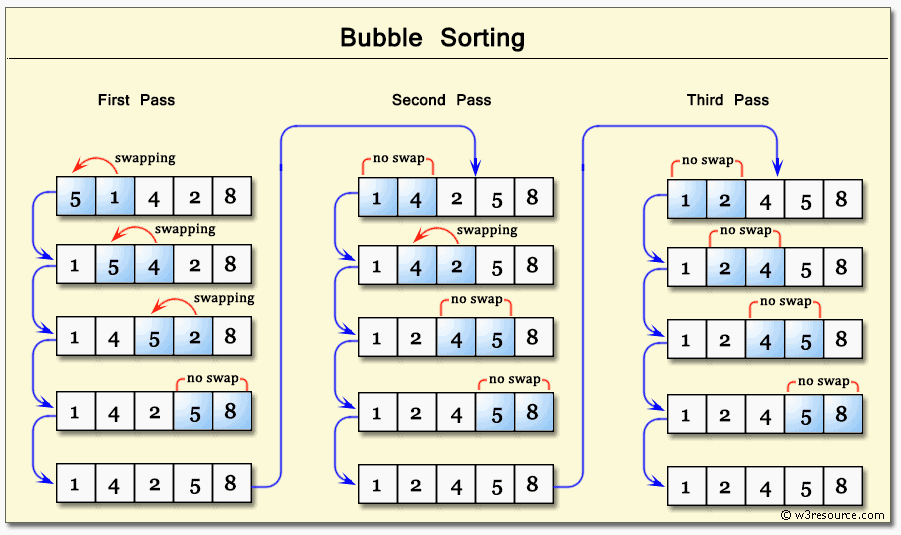 Bubble is a very basic sorting algorithm
Bubble is a very basic sorting algorithm
in Computer Programming. It is also known as a sinking sort. Here,
elements located beside each other in a data structure (such as an
array) are continuously compared until the order of the list is
corrected. The elements will be exchanged only if two adjacent
elements are in the wrong order.
It is named as bubble sort because the largest element in the
data structure is placed on top. Or see it the other way that the
largest of all elements sink to the top of the list, just the way
bubbles in water do. Hence, the name is bubble sort.
41. Do explain Selection
Sorting.
Selection sorting is another simple sorting technique for
computer programming. Unlike bubble sorting, in selection sorting,
the list of elements is divided into two portions. One part holds
the sorted elements, whereas the other one contains the unsorted
elements. At the beginning of the sorting, sorting elements are
zero, and unsorted elements are the maximum.
The selection process starts with the element that holds the
smallest value. And exchange its place with the leftmost element of
the unsorted list. Thus becoming a part of the sorted list. Then
the next smallest value is swapped in the same process until the
list is organized.
42. What is the term “undefined value”
means in programming?
The term undefined value in computer programming refers to such
a condition where the value of a variable cannot be defined. In
other words, undefined values are not correct. Often they hold an
infinite value or values that are not practically expressive.
For example, when you divide the full integer by zero, we all know
that the result is infinite. However, your compiler will show an
error message. And hence, the result will be undefined.
Often undefined value is mistaken with other conditions such as
empty values or strings; even boolean expressions are also
sometimes confused with undefined values.
43. What does a palindrome program
do?
 A palindrome can be a word or phrase. When a
A palindrome can be a word or phrase. When a
word or phrase can be read the same way backward as the way it is
read in forward, it is called a palindrome. A palindrome can be
words as well as be numbers. For example, the word “WOW” is a
palindrome. It is read the same both in forward and backward. The
same way, 11, 22, 33, and many other numbers are also the same when
reading backward and forward.
A palindrome program will make sure if a word or number is
palindrome or not.
44. Explain Huffman’s algorithm and its
function.
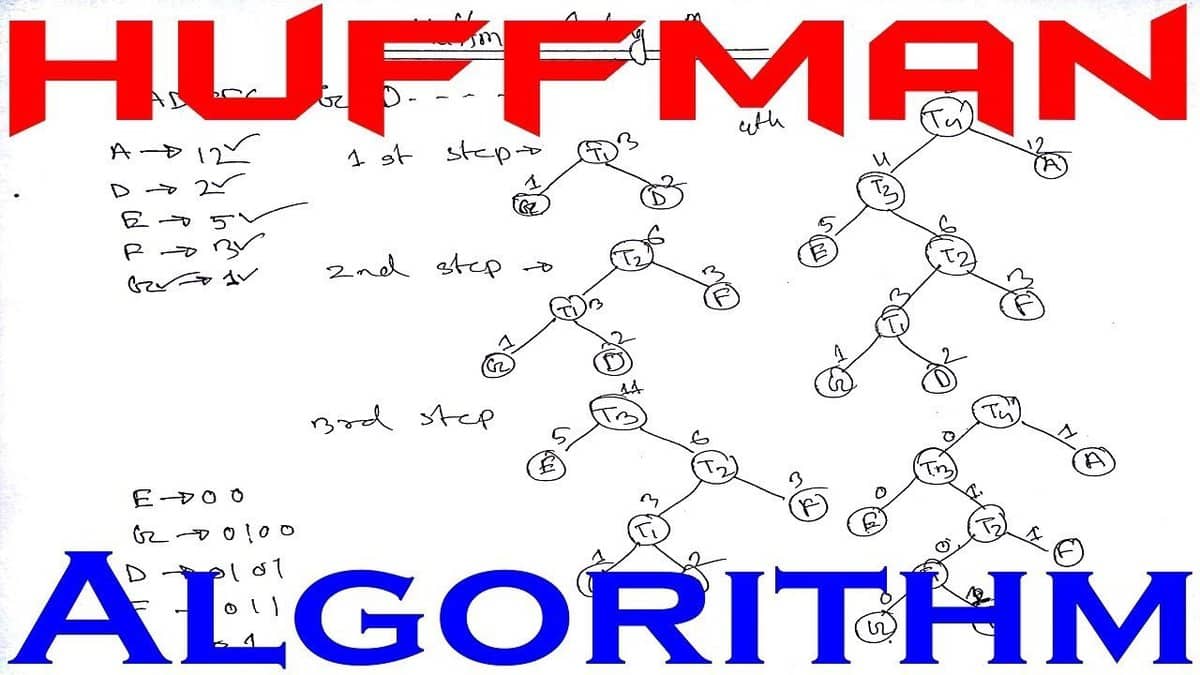 Huffman’s algorithm, also known as
Huffman’s algorithm, also known as
Huffman’s coding, is a precise code for lossless data.compression.
Huffman code is a prefix code. And it is widely used in a variety
of compression types, such as Winzip, gzip, and image formats such
as JPEG and PNG.
The main purpose of Huffman is to widen the binary trees.
Huffman algorithm makes the use of a table that holds the complete
number of times for each and every data element.
45. What is the Fibonacci
search?
In computer programming, the Fibonacci search[5]
makes the use of Fibonacci numbers to search an item in a sorted
array. So, basically, the Fibonacci search is a search technique
that works based on the comparison.
In order to find a particular element in a sorted array, the
Fibonacci search uses a divide and conquer algorithm. This divides
and conquers algorithm indicates a few reasonable locations of the
specific element using Fibonacci numbers.
46. What is a linked list?
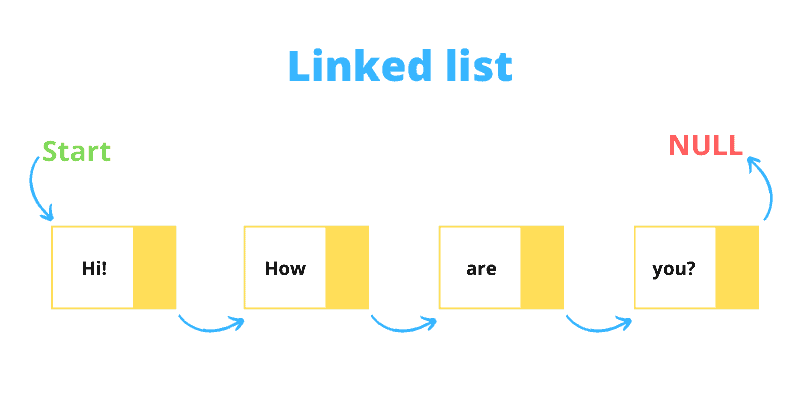 A linked list in computer programming is a
A linked list in computer programming is a
form of linear data structure. Here, each element is individual. In
a linked list, elements do not share any physical memory location;
rather, they are connected through pointers. Hence, the name is a
linked list.
Unlike other data structures, here each and every element of the
list is configured with two things – 1) the data itself, 2) a
reference to the next element node. The first node points to the
next one, and that’s how the link method goes on. However, the last
one points to a null reference.
47. What is data abstraction?
Data abstraction in computer programming is a particular way of
data simplification. It depletes specific parts of data and helps
to turn it into an easily maintainable form. Data abstraction, in
other words, cuts down some specific characteristics from data and
reduces them into some useful characteristics.
Note, it is the initial step to the decoration of the
database.
48. Please explain a recursive
function.
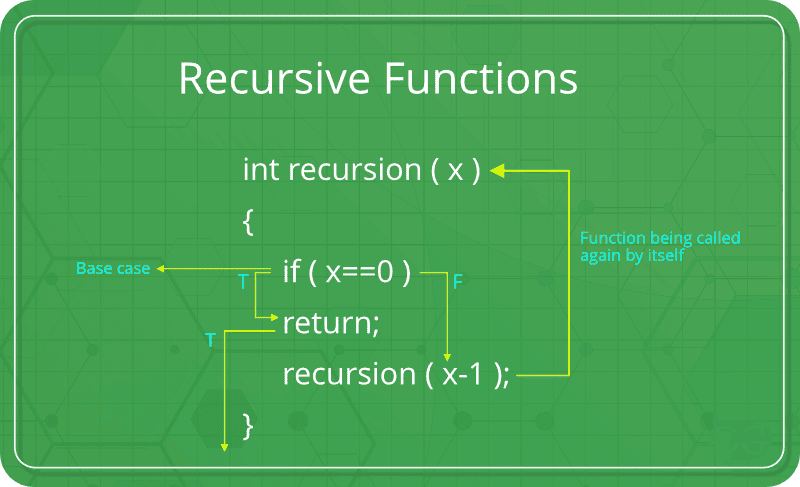 A recursive function is such a function
A recursive function is such a function
that calls itself. Recursive functions allow themselves to repeat
themselves again and again during the execution period. Recursive
functions focus on closing conditions. And these functions also
make the use of stacks.
49. What is a Binary search?
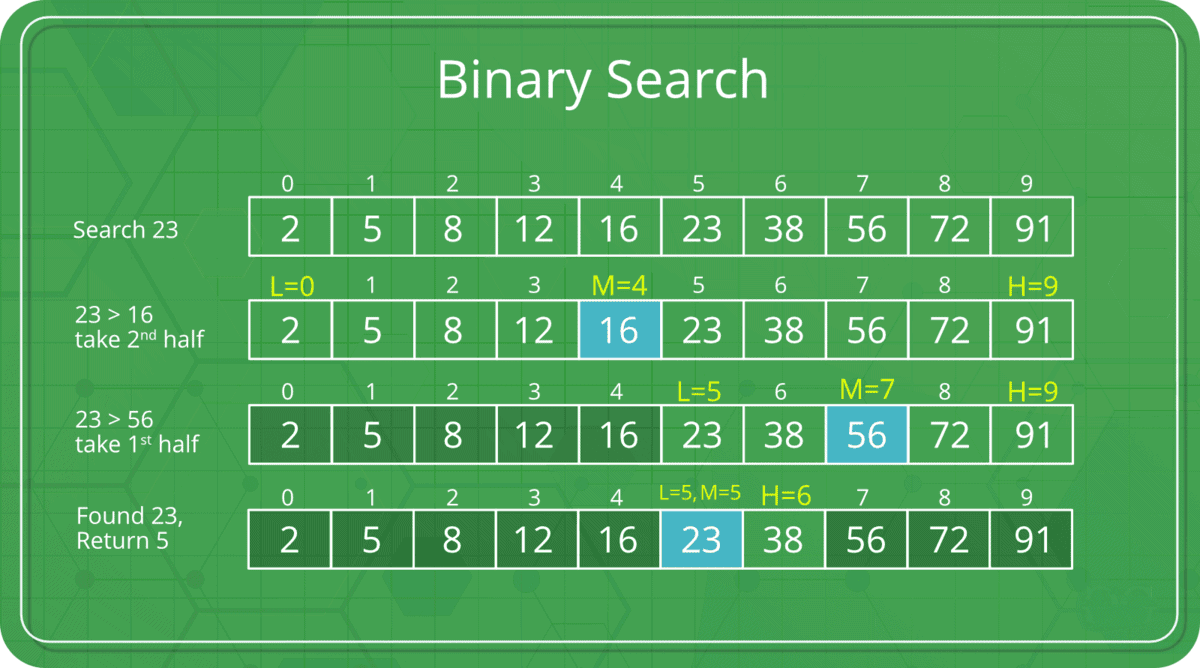 In the world of computer programming, binary
In the world of computer programming, binary
search is also known as binary chop or logarithmic search. It is a
search technique for the sorted array. Binary search helps to
locate the position of specific value in a sorted array.
In a sorted array, the binary search starts with the element in
the middle. If the element in the middle is, however, doesn’t hold
the target value, then the process continues with whether the lower
half or upper half of the array. If the proper solution is not
found, then the same procedure keeps repeating.
50. How does dynamic memory allocation
help to maintain data?
Yes, I do. Dynamic memory allocation is a process of assigning
memory during the runtime. Dynamic memory allocation piles basic
types of structured data. Apart from storing structured data, it
also merges individually issued structured blocks in order to
develop composite structures.
These composite structures are flexible to easy expansion and
contraction as required. Note, along with many other benefits of
dynamic memory allocation, one major one is, it saves a lot of
memory usage.
Final Thoughts
Here ends our list of 50 frequently asked programming interview
questions. Even if you are a new graduate, our list will help you
to be one step ahead of other freshers on the board. However, ours
is definitely a good selection of the most asked questions in a
programming interview board. If you feel like we are missing any
important interview questions, do let us know in the comment
section. Also, don’t forget to share our content with your
friends.
References
- ^
Top 20
Highest Paying Computer Science Jobs in 2020
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Top 20
Most Popular Programming Languages To Learn For Your Open-source
Project (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
The 20
Best Linux Debuggers for Modern Software Engineers
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Top 15
Best Embedded Systems Programming Languages
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Fibonacci search
(en.wikipedia.org)
Read more https://www.ubuntupit.com/frequently-asked-programming-interview-questions-and-answers/