Redmi smartphone, you should immediately stop using its built-in
MI browser or the Mint browser available on Google
Play Store for non-Xiaomi Android devices.
That’s because both web browser apps created by Xiaomi are
vulnerable to a critical vulnerability which has not yet been
patched even after being privately reported to the company, a
researcher told The Hacker News.
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2019-10875 and
discovered by
security researcher Arif Khan, is a browser address bar
spoofing issue that originates because of a logical flaw in the
browser’s interface, allowing a malicious website to control URLs
displayed in the address bar.
[1][2]
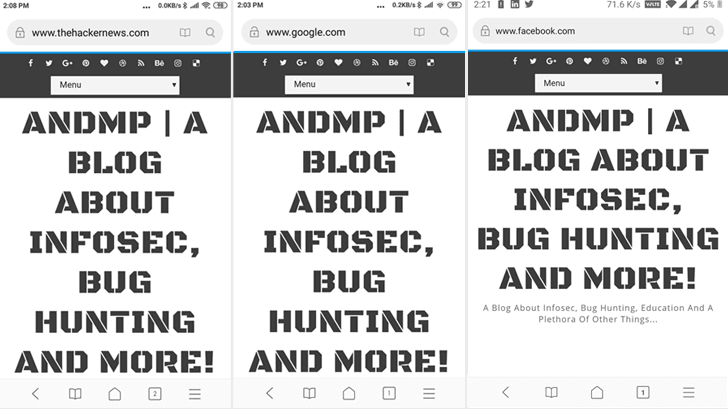
Since the address bar of a web browser is the most reliable and
essential security indicator, the flaw can be used to easily trick
Xiaomi users into thinking they are visiting a trusted website when
actually being served with a phishing or malicious content, as
shown in the video demonstration below.
The phishing attacks today are more sophisticated and
increasingly more difficult to spot, and this URL spoofing
vulnerability takes it to another level, allowing one to bypass
basic indicators like URL and SSL, which are the first things a
user checks to determine if a site is fake.
The Hacker News has independently verified the vulnerability
using a PoC the researcher shared with our team and can confirm it
works on the latest versions of both web browsers—MI Browser
(v10.5.6-g) and Mint Browser (v1.5.3)—that are available at
the time of writing.
Hacker News that the issue only affects the international variants
of both the web browsers, though the domestic versions, distributed
with Xiaomi smartphones in China, do not contain this
vulnerability.
“The thing that struck me most was that only their overseas or,
international versions were having this security bug and not their
Chinese or, domestic versions. Was it done deliberately thus?” Arif
told The Hacker News in an email.
“Are Chinese device manufacturers intentionally making their OS,
applications, and firmware vulnerable for their international
users?”
issue, Xiaomi rewarded the researcher with a bug bounty, but left
the vulnerability unpatched.
“The vulnerability impacts millions of users globally yet the
bounty offered as such was, $99 (for Mi Browser) and another $99
(for Mint Browser),” the researcher said.
report for additional comment and learn if the company has plans to
release a patched version anytime soon, but the mobile vendor
provided a weird response.
“I would like to inform you that as of there is no official update
regarding the issue. However, would request you to stay connected
with the forum page for further details in this regards,” the
company said.
have identified in pre-installed apps on more than 150 million
Android devices manufactured by Xiaomi. Just yesterday, The Hacker
News published details of a report explaining how attackers could
have turned a pre-installed
security app on Xiaomi phones, called Guard Provider, into
malware by exploiting multiple vulnerabilities in the app.
The bottom line: Android users are highly advised to use
modern web browsers that are not affected by this vulnerability,
such as Chrome or Firefox.
Besides this, if you are using Microsoft Edge or
Internet Explorer browser[4]
on your desktop, you should also avoid using them since both
browsers also contain a critical vulnerability which has not yet
been patched by the tech giant.
References
- ^
discovered
(www.andmp.com) - ^
Arif Khan
(twitter.com) - ^
pre-installed security app on Xiaomi
phones (thehackernews.com) - ^
Microsoft Edge or Internet Explorer
browser (thehackernews.com)
Read more http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/TheHackersNews/~3/nKUWe0PTv88/xiaomi-browser-vulnerability.html