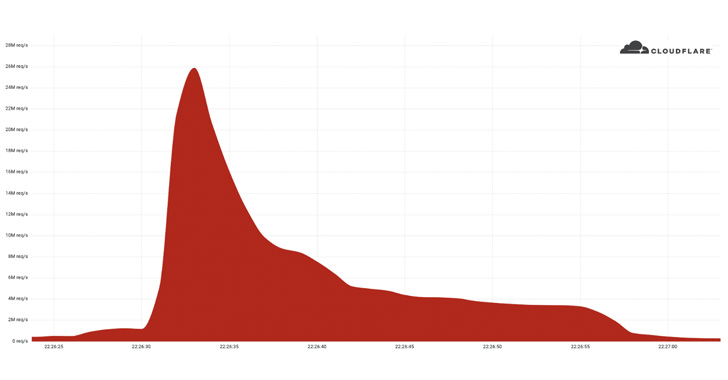
Cloudflare on Tuesday disclosed that it had acted to prevent a
record-setting 26 million request per second (RPS) distributed
denial-of-service (DDoS) attack last week, making it the largest
HTTPS DDoS attack detected to date.
The web performance and security company said the attack was
directed against an unnamed customer website using its Free plan
and emanated from a “powerful” botnet of 5,067 devices, with each
node generating approximately 5,200 RPS at peak.
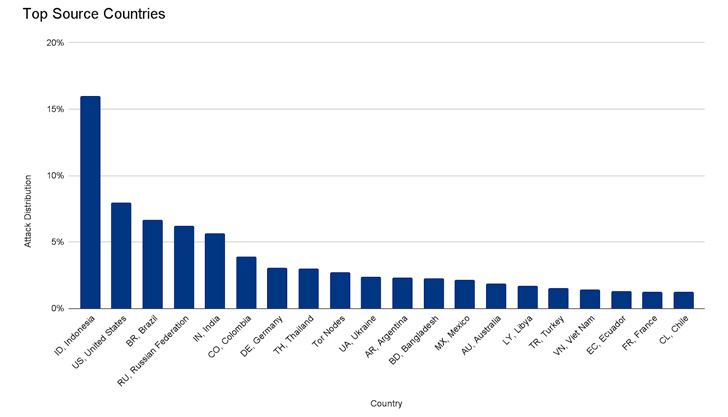
The botnet is said to have created a flood of more than 212
million HTTPS requests within less than 30 seconds from over 1,500
networks in 121 countries, including Indonesia, the U.S., Brazil,
Russia, and India. Roughly 3% of the attack came through Tor
nodes.
The attack “originated mostly from Cloud Service Providers as
opposed to Residential Internet Service Providers, indicating the
use of hijacked virtual machines and powerful servers to generate
the attack — as opposed to much weaker Internet of Things (IoT)
devices,” Cloudflare’s Omer Yoachimik said[1].
Launching HTTPS-based DDoS attacks tend to be more expensive
computationally owing to the higher cost associated with
establishing a secure TLS encrypted connection.
This is the second such volumetric HTTPS DDoS attack to be
thwarted by Cloudflare in as many months. In late April 2022, it
said it staved off[2]
a 15.3 million RPS HTTPS DDoS attack aimed at a customer operating
a crypto launchpad.
According to the company’s DDoS attack trends report for Q1
2022, volumetric DDoS attacks over 100 gigabits per second (gbps)
surged by up to 645% quarter-on-quarter.
“Attacks with high bit rates attempt to cause a
denial-of-service event by clogging the Internet link, while
attacks with high packet rates attempt to overwhelm the servers,
routers, or other in-line hardware appliances,” the researchers
said[3].
“In such a case, packets are ‘dropped,’ i.e., the appliance is
unable to process them. For users, this results in service
disruptions and denial of service.”
References
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/06/cloudflare-saw-record-breaking-ddos.html