The botnet behind the largest HTTPS distributed
denial-of-service (DDoS) attack in June 2022 has been linked to a
spate of attacks aimed at nearly 1,000 Cloudflare customers.
Calling the powerful botnet Mantis, the web
performance and security company attributed it to more than 3,000
HTTP DDoS attacks against its users.
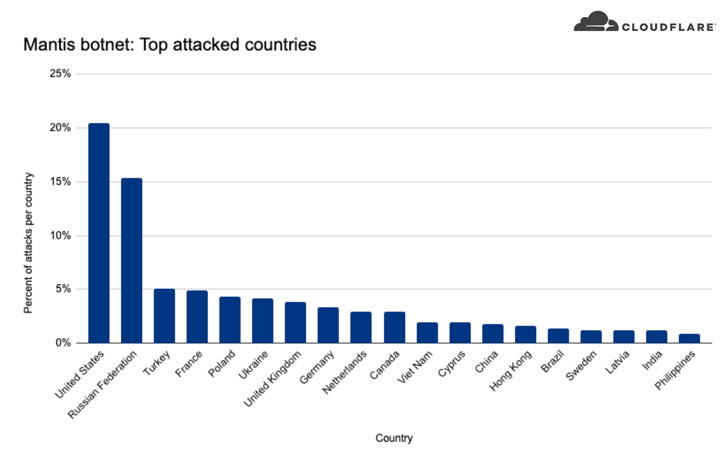
The most attacked industry verticals include internet and
telecom, media, gaming, finance, business, and shopping, of which
over 20% of the attacks targeted U.S.-based companies, followed by
Russia, Turkey, France, Poland, Ukraine, the U.K., Germany, the
Netherlands, and Canada.
Last month, the company said it mitigated[1]
a record-breaking DDoS attack aimed at an unnamed customer website
using its Free plan that peaked at 26 million requests per second
(RPS), with each node generating approximately 5,200 RPS.
The tsunami of junk traffic lasted less than 30 seconds and
generated more than 212 million HTTPS requests from more than 1,500
networks in 121 countries, topped by Indonesia, the U.S., Brazil,
Russia, and India.
“The Mantis botnet operates a small fleet of approximately 5,000
bots, but with them can generate a massive force — responsible for
the largest HTTP DDoS attacks we have ever observed,” Cloudflare’s
Omer Yoachimik said[2].
Mantis stands out for a number of reasons. The first is its
ability to carry out HTTPS DDoS attacks, which are expensive in
nature due to the computational resources required to establish a
secure TLS encrypted connection.
Secondly, unlike other traditional botnets that rely on IoT
devices such as DVRs and routers, Mantis leverages hijacked virtual
machines and powerful servers, equipping it with more
resources.
These volumetric attacks aim to generate more traffic than the
target can process, causing the victim to exhaust its resources.
While adversaries have traditionally utilized UDP to launch
amplification attacks, there has been a shift to newer TCP reflected amplification
vectors[3] that make use of
middleboxes.
Microsoft, in May 2022, disclosed that it prevented about
175,000 UDP reflected amplification attacks over the past year that
were aimed at its Azure infrastructure. It also observed a TCP
reflected amplification attack on an Azure resource in Asia that
reached 30 million packets per second (pps) and lasted 15
minutes.
“Reflected amplification attacks are here to stay and pose a
serious challenge for the internet community,” the Azure Networking
Team noted[4]. “They continue to
evolve and exploit new vulnerabilities in protocols and software
implementations to bypass conventional countermeasures.”
References
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/07/mantis-botnet-behind-largest-https-ddos.html