Two new security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in Rockwell
Automation’s programmable logic controllers (PLCs[1]) and engineering
workstation software that could be exploited by an attacker to
inject malicious code on affected systems and stealthily modify
automation processes.
The flaws have the potential to disrupt industrial operations
and cause physical damage to factories in a manner similar to that
of Stuxnet and the Rogue7 attacks[2], operational technology
security company Claroty said.
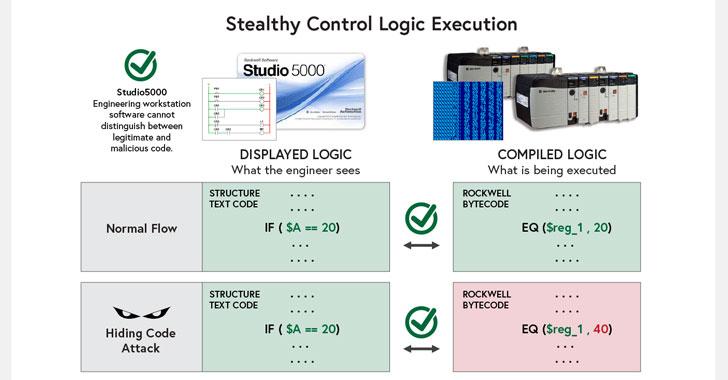
“Programmable logic and predefined variables drive these
[automation] processes, and changes to either will alter normal
operation of the PLC and the process it manages,” Claroty’s Sharon
Brizinov noted[3]
in a write-up published Thursday.
The list of two flaws is below –
- CVE-2022-1161[4] (CVSS score: 10.0) – A
remotely exploitable flaw that allows a malicious actor to write
user-readable “textual” program code to a separate memory location
from the executed compiled code (aka bytecode). The issue resides
in PLC firmware running on Rockwell’s ControlLogix, CompactLogix,
and GuardLogix control systems. - CVE-2022-1159[5] (CVSS score: 7.7) – An
attacker with administrative access to a workstation running Studio
5000 Logix Designer application can intercept the compilation
process and inject code into the user program without the user’s
knowledge.
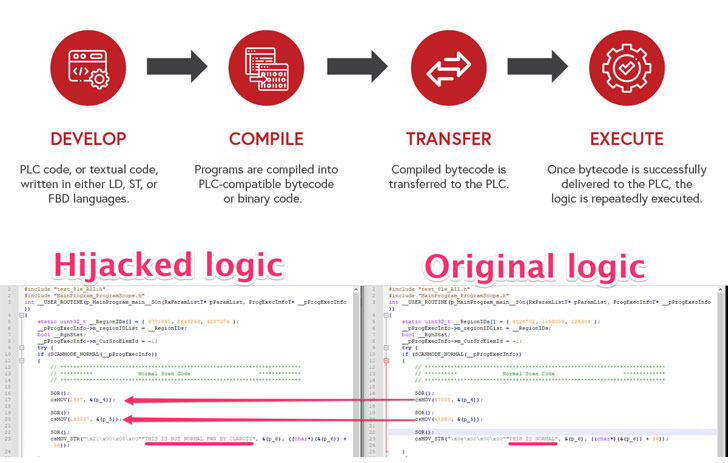
Successful exploitation of the defects could allow an attacker
to modify user programs and download malicious code to the
controller, effectively altering the PLC’s normal operation and
allowing rogue commands to be sent to the physical devices
controlled by the industrial system.
“The end result of exploiting both vulnerabilities is the same:
The engineer believes that benign code is running on the PLC;
meanwhile, completely different and potentially malicious code is
being executed on the PLC,” Brizinov explained.
The severity of the flaws has also prompted an advisory[6]
from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
(CISA) that outlines mitigation steps users of the affected
hardware and software can take for a “comprehensive
defense-in-depth strategy.”
References
- ^
PLCs
(en.wikipedia.org) - ^
Rogue7
attacks (thehackernews.com) - ^
noted
(claroty.com) - ^
CVE-2022-1161
(www.cisa.gov) - ^
CVE-2022-1159
(www.cisa.gov) - ^
advisory
(www.cisa.gov)
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/04/critical-bugs-in-rockwell-plc-could.html