In Linux, the Secure Shell (SSH) is a method where you can
access another computer through a secure and two-way encrypted
communication system over the internet. By enabling the SSH service
in Linux, you can use the SSH protocol as an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) server or,
you can get remote access to another Pc. Enabling SSH service can
connect your device to another device or server through a secure
tunnel where your identity and data transmissions are totally safe
and encrypted. If you are a network administrator, you must know
how to enable and configure the SSH service in Linux. [1]
SSH Service in Linux
In Linux, the SSH service works a method called end-to-end
encryption, where one user has a public key, and another user holds
a private key. Data transmission can occur when both users enter
the right encryption keys. The SSH functions through the terminal
command-line interface. Most of the Apache servers and Nginx servers[2]
use the SSH service to get remote access and provide service to
their clients. In this post, I will show how to enable and use the
SSH service in several Linux distros.
1. Installing the SSH Service on
Ubuntu Linux
The SSH service is installed by default in all Linux or
Unix-like operating systems. You can check whether the SSH service
is installed inside your Linux machine or not by checking the SSH
version. If you find your Ubuntu has an SSH installed, you are good
to go. If you cannot find the secure shell service in your Ubuntu
Linux, you can install it by the apt-get[3]
install command.
$ ssh -V
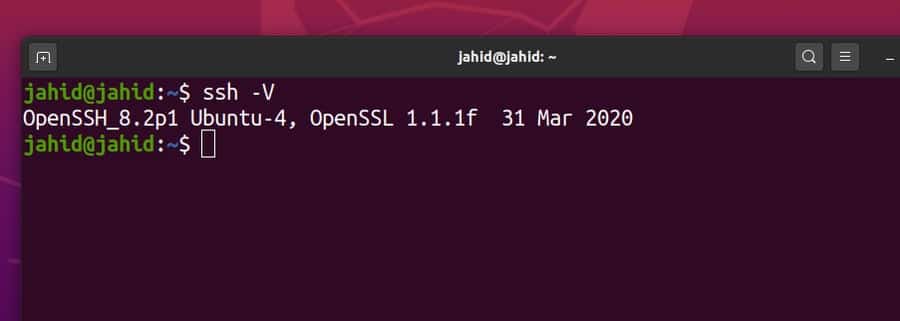
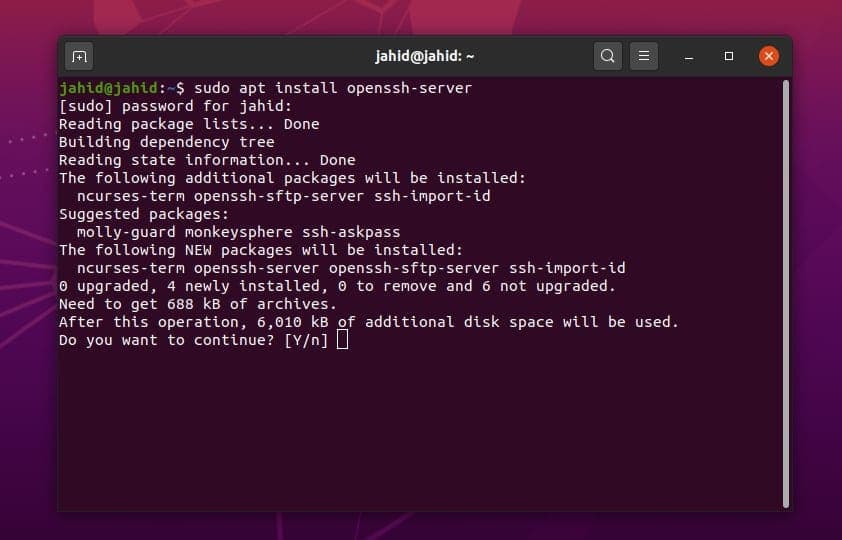
Before installing any packages, you should update and upgrade
the Ubuntu repository. Then install the Openssh Server package with
the terminal shell command. All the terminal command lines are
given below.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt upgrade
$ sudo apt install openssh-server
2. Enabling SSH on Red Hat Linux
and CentOS
Red Hat Linux was mainly created for workload distribution,
cloud and docker utilization, and evolution purpose. Here are the
terminal command lines to check, install, start, and enable the SSH
service on Red Hat Linux. Like other Linux distros, Red Hat also
uses the port 22 to establish SSH service. You may also need to
allow the firewall access for SSH service on CentOS and Red Hat
Linux.
$ dnf install openssh-server
$ yum install openssh-server
$ systemctl start sshd
$ systemctl status sshd
$ systemctl enable sshd
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ssh
3. Enabling SSH on Arch
Linux
The Arch Linux uses the package manager (packman[4]) command to install any
application. First, you need to update the system repository of
Arch Linux. Then you can install the OpenSSH service on Arch Linux
through the packman commands. You can start or stop any SSH
service, check the SSH status, and disable the SSH service on Arch
Linux using the systemctl terminal command.
$ sudo pacman -Sy
$ sudo pacman -S openssh
$ sudo systemctl status sshd
$ sudo systemctl start sshd
$ sudo systemctl status sshd
$ sudo systemctl stop sshd
$ sudo systemctl enable sshd
$ sudo systemctl disable sshd
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
To configure the SSH service script on Arch Linux, you need to
open the configuration file from the /etc/ssh/
directory.
$ man sshd_config / config files
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
4. Enabling SSH on Fedora
Linux
Before installing the SSH service on Fedora Linux, let us check
whether the SSH service is already installed inside the machine or
not. We will use the grep terminal command[5]
to check the availability of SSH service on Fedora Linux. Fedora
Linux also uses port 22 to establish secure shell connections.
Moreover, we can check the total SSH service status by using the
systemctl command on the terminal shell. Besides
these, you can start, stop, enable, and disable the secure shell on
Fedora Linux using the terminal command lines that are given
below.
$ rpm -qa | grep openssh-server
$ sudo dnf install -y openssh-server;
$ sudo systemctl status sshd
$ sudo ss -lt
$ sudo systemctl start sshd.service;
$ sudo systemctl stop sshd.service;
$ sudo systemctl disable sshd.service;
A Few Primary Commands of SSH
Service
Till now, we have gone through the process of how to enable and
configure the SSH service on Linux distributions. Now, we will see
how to run some basic commands of SSH service on Linux. Here, I
will show the primary rules of establishing a secure service,
getting firewall access, and tunnel forwarding on Linux. Once you
get to know the fundamental phenomena of SSH service, you will be
able to enable and configure other SSH services on your own.
Task 1: Basic Commands of SSH
Service on Linux
Once the SSH service is installed inside your Linux machine, you
can now check the system status, enable the SSH service, and get
started with the secure shell system. Here, some basic SSH commands
are given. You can also turn off the SSH system if you do not need
it.
$ sudo systemctl status ssh
$ sudo service ssh status
$ sudo systemctl enable ssh
$ sudo systemctl start ssh
$ sudo systemctl stop ssh
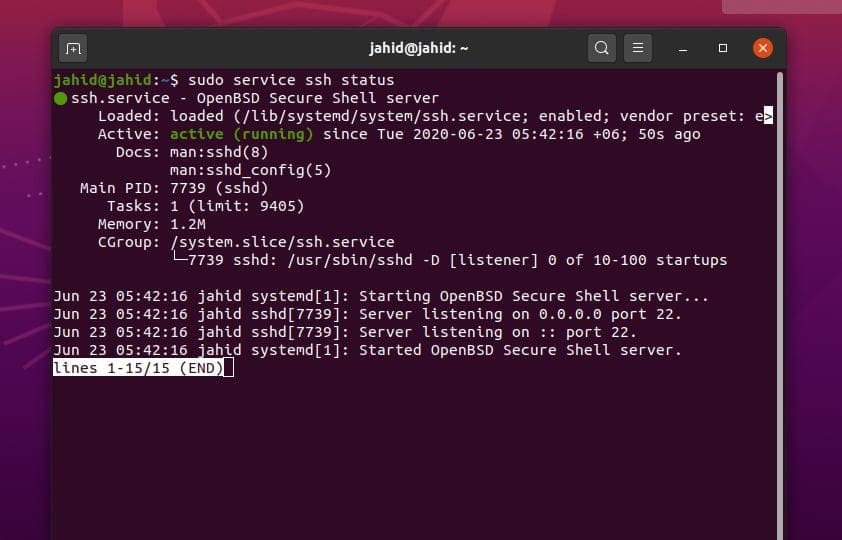
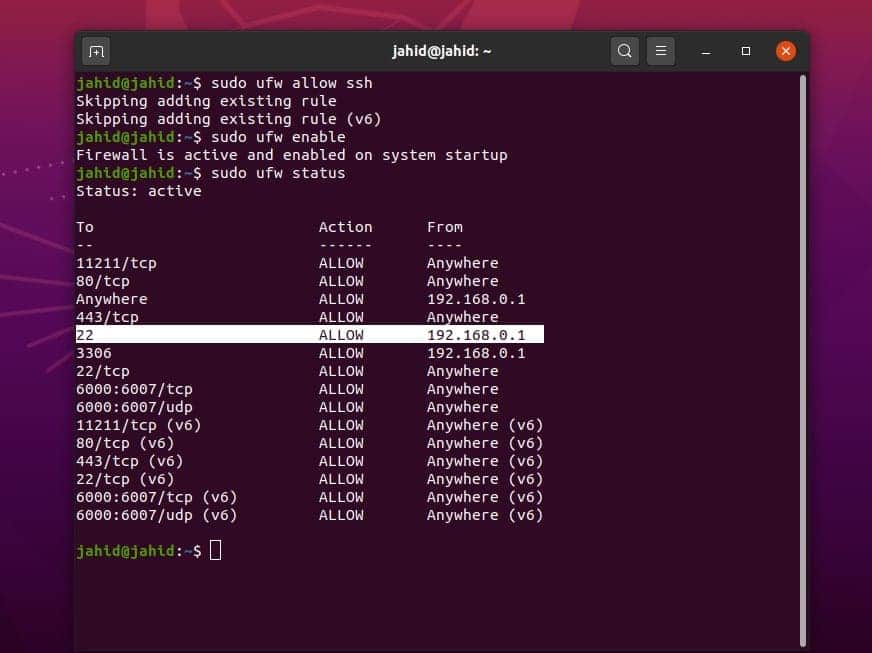
Task 2: Getting Firewall Access
for SSH Service
When you are dealing with an internet transfer protocol, you
need to get the firewall access. Otherwise, the firewall may block
and interrupt your connection. Here, I am using the UFW firewall
system to configure the SSH service on Linux. After enabling the
UFW firewall, you may now check the firewall status. The firewall
system will monitor all the incoming and outgoing networks of your
device.
$ sudo ufw allow ssh
$ sudo ufw enable
$ sudo ufw status
Task 3: Connecting to a Specific
IP through SSH Service on Linux
If you are using a static IP address for the secure shell
connection, you can set rules for the specific network and port.
For SSH service, the default port is 22. You can change the port if
necessary. We will run the vvv command to check and
set the SSH protocol against a specific IP address. In my case, I
am trying to connect the localhost network. Those who
don’t know how to get a localhost network in Linux can see the
procedures of how to install the Apache[6]
server on Linux.
$ vvv-ssh
$ ssh -vvv localhost
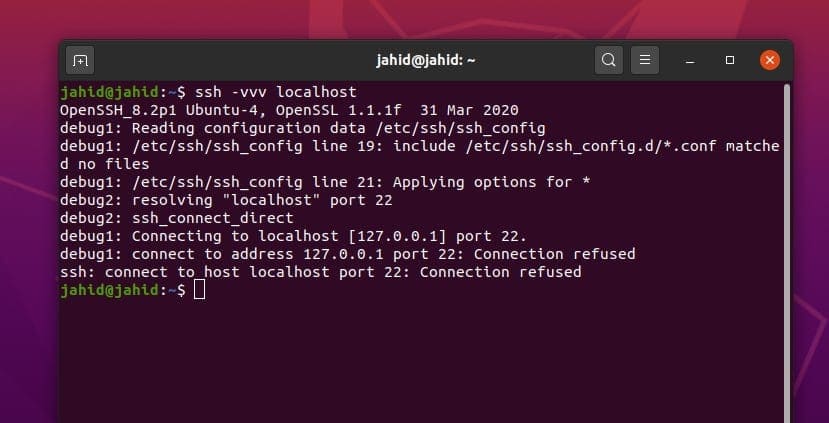
Let, you know your username and the static IP address, you can
now build a secure shell network from your Linux machine to another
device. If you don’t know your username, you may follow the
terminal command given below.
$ whoami
To get connected to your localhost address, use these terminal
command lines on your Linux terminal shell. I have demonstrated
several methods of accessing the SSH service with a specific
username and an IP address.
$ ssh
$ ssh [email protected]_address
$ ssh [email protected]
$ sss [email protected]
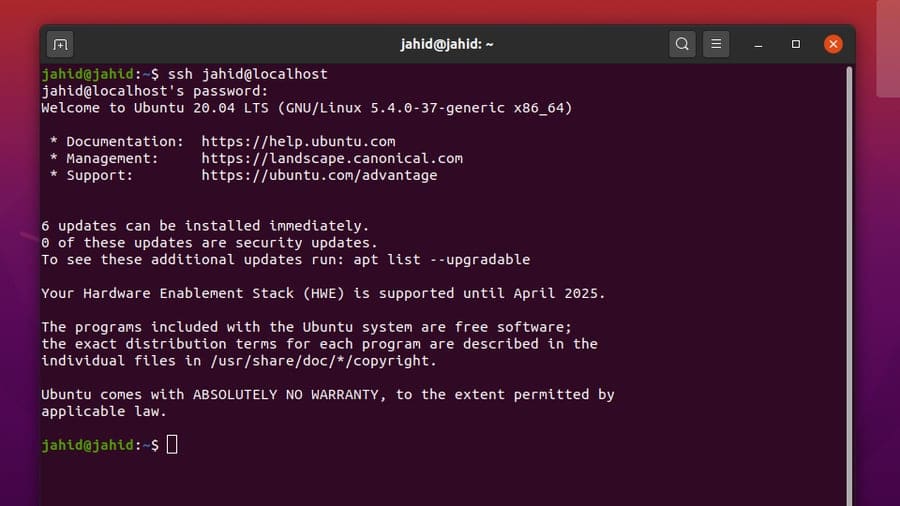
To find your IP address, you can use the basic net-tool commands[10] to get your internet
protocol details. And now, I assume you know both your IP address
and username. Here is the method to connect to a specific IP
address. I may mention that you can also connect to a public IP
address through an SSH service on Linux.
$ ip a
$ ifconfig
$ ssh [email protected]
[11]
$ ssh [email
protected][12]_ip_address
Task 4: Configuring Port
Forwarding on Linux
We already know that internet protocols work with an assigned IP
address and a port number. The term port forwarding or tunneling is
the method of bypassing the data packets through a tunnel where
your digital footprints are hidden and secured. The port forwarding
methods are applied when you face some firewall protection or any
restriction to reach your destination server.
But, before you start tunneling, make sure that you have enough
open ports available to forward ports.
There are various types of port forwarding, such as local
forwarding, virtual forwarding, and dynamic port forwarding.
[13]
Here, I am going to describe the local port forwarding, the
dynamic port forwarding, and the remote port forwarding system
through the SSH service on Linux. To enable port forwarding, we
need to check the configuration file of SSH service. We can find
the SSH configuration file under the root/etc/ssh
directory.
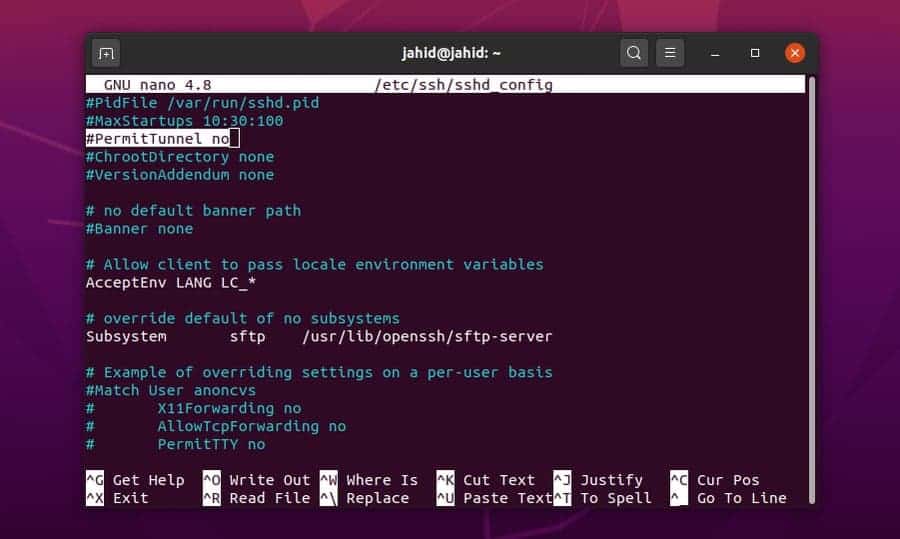
We can directly open the configuration script through the Nano
editor. Here, it would be best if you changed the value of
PermitTunnel to yes, and the GatewayPorts to. Then save the script file. After configuring the SSH
yes
script, you must have to restart the SSH service on your Linux
machine.
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
$ nano ~/.ssh/config
$ vi $HOME/.ssh/config
$ sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
GatewayPorts yes
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
$ sudo service sshd restart
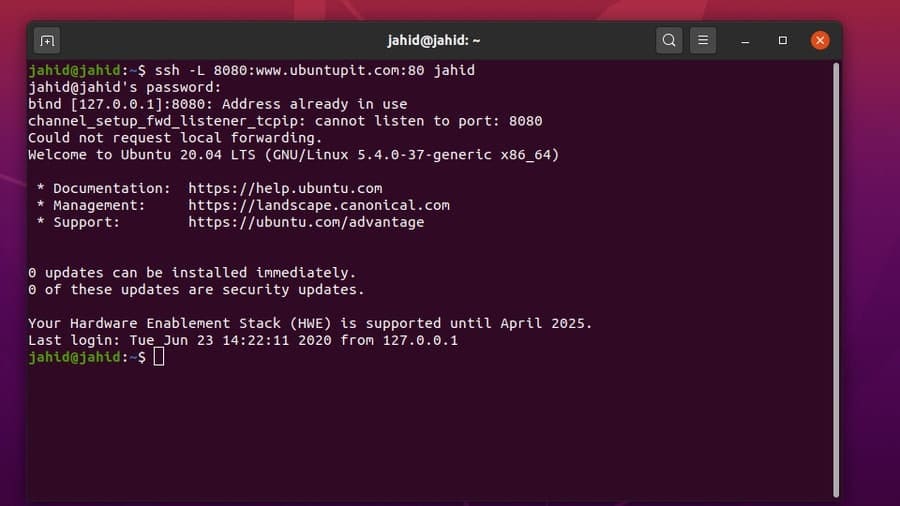
Now, let you want to forward an IP address from your local Linux
machine to the server through the SSH tunnel service. All you need
to do is, open the terminal shell and type ssh then type your
[email protected][14]_address.
$ ssh [email protected]
[15]_address.com
For remote port forwarding, you may use the same procedure of
SSH service in Linux. But if you want to do the process in the
background, you have to add the -f-N syntax
before your server address. You can also set dynamic and local port
forwarding through the SSH service in Linux.
$ ssh -f -N [email protected]
[16] -R 5000:localhost:3000
$ ssh -f -N -D 1080 [email
protected][17]
$ ssh -L 8080:www.ubuntupit.com:80 jahid
$ ssh -R 5900:localhost:5900 jahid
To allow the port mapping application for specific software, you
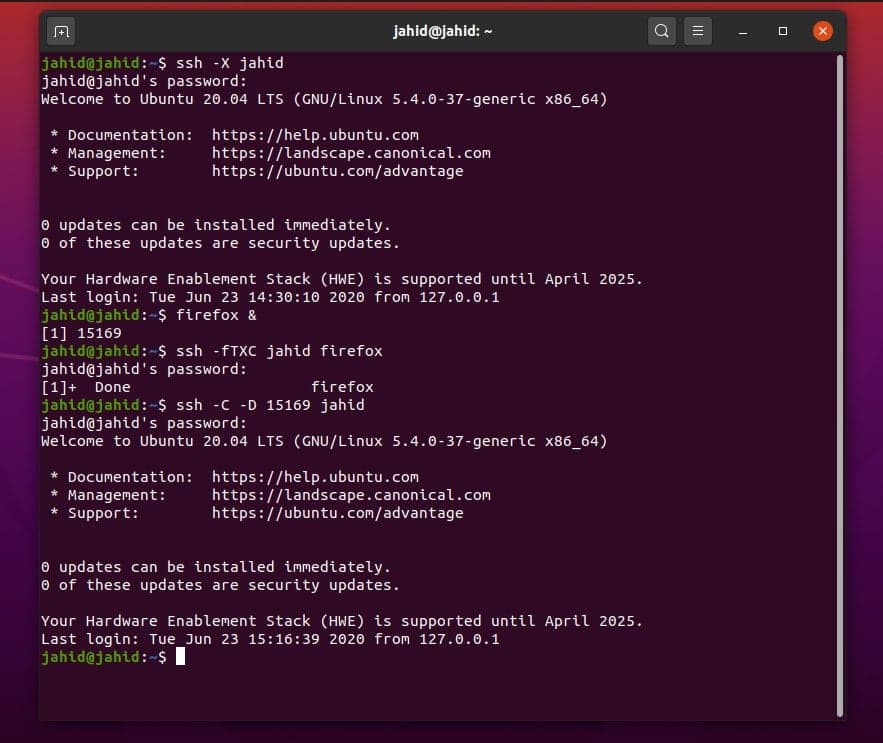
can use the SSH service in your Linux machine. Here, I am using
port 15169 for Firefox. Then, you may need to configure the Firefox
Networking too.
$ ssh -X jahid
$ firefox &
$ ssh -fTXC jahid firefox
$ ssh -C -D 15169 jahid
Task 5: Enabling & Authorizing the
SSH System
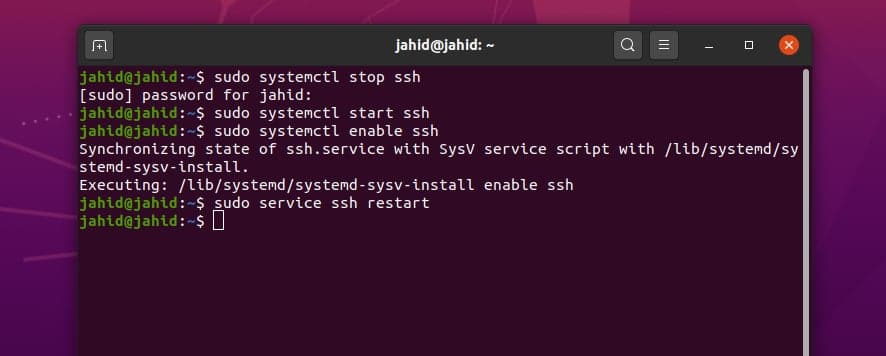
In Linux, you can use the systemctl command to
start, stop, enable, disable, and restart the SSH service. After
enabling the SSH service, you may now check the port that will be
used to establish the secure shell connections. We can check the
port number from the SSH configuration script file. The SSH
configuration file is located in the /etc/ssh/
directory. We can directly open the configuration file using the
Nano script editor.
$ sudo systemctl stop ssh
$ sudo systemctl start ssh
$ sudo systemctl enable ssh
$ sudo service ssh restart
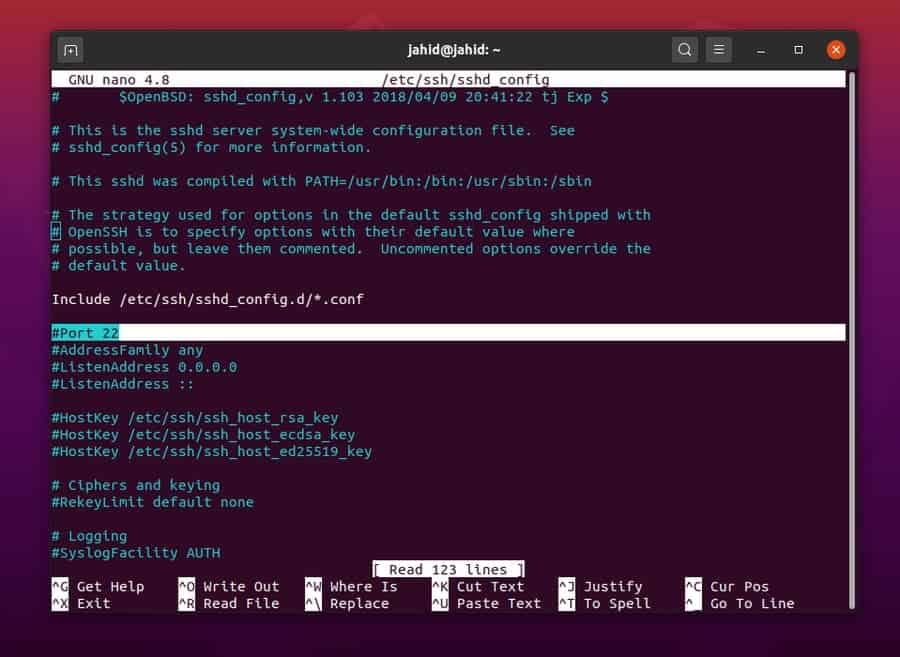
Once the script is opened, you will be able to see the
AddressFamily, Port Number, Listening IP addresses, and other log
files. If you find something is wrong in the configuration script,
you can also reset the configuration file.
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
$ /etc/init.d/sshd restart
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
$ /etc/init.d/sshd restart
$ vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
You can also try other methods to enable and configure the SSH
service on Linux. This method will ask the user to create a
directory to configure and store the data. You can create a
specific SSH service for every user on Linux. I will use the
touch command to configure the script file. Here, I am
using my hostname, be mindful of using your hostname. Then restart
the SSH service.
$ /etc/ssh/ssh_config
$ ~/.ssh/config or $HOME/.ssh/config
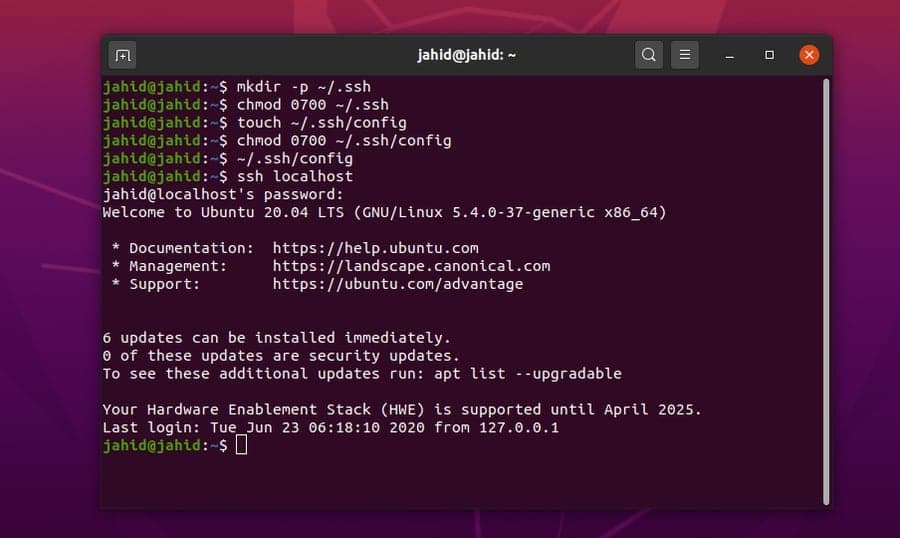
$ mkdir -p ~/.ssh
$ chmod 0700 ~/.ssh
$ touch ~/.ssh/config
$ chmod 0700 ~/.ssh/config
~/.ssh/config
$ ssh UbuntuPIT
$ /etc/init.d/sshd restart
Additional Help to Manage the
Secure Shell Services
Maintaining a secure and duplex network connection can be a bit
tricky, sometimes. As a Linux network administrator, you must know
how to handle the unforeseen problems of secure shell operations.
You need to know what to do when suddenly the running SSH service
gets disconnected. You also need to know how to install the SSH
service on the client’s device.
$ sudo apt-get remove openssh-client openssh-server
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-client openssh-server
To get more help about the SSH service on Linux, you may use the
default help function from the terminal shell. Here are some basic
SSH service-related terminal commands which you may find useful and
handy to verify SSH and SSHD on Linux.
$ ssh –help
$ which ssh
$ which sshd
$ whereis ssh
$ ssh -v localhost
Ending Thoughts
Secure shell service is the most effective and powerful
application to connect two devices remotely. Though, some graphical
user interface based remote access applications is also available
for Linux. But, in the long race, the SSH service is way better and
reliable for Linux. In this post, I have described all the possible
ways of enabling SSH service in Linux. I’ve also demonstrated the
fundamental ideas of port forwarding and end-to-end encryption.
If you are a sysadmin, you must know how essential it is to have
complete knowledge of the SSH service. So, if you love this
article, you can share this post on your social media. And we also
encourage you to write your opinions related to this post in the
comment section.
References
- ^
Best
Linux FTP Client: Top 10 Reviewed for Linux Geeks
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
25 Must
Know Nginx Commands for Developers and Admins
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
apt-get
(linux.die.net) - ^
packman
(packman.links2linux.org) - ^
50
Productive and Practical grep Command for Linux Enthusiasts
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Apache
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
net-tool commands
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
open
ports (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com)
Read more https://www.ubuntupit.com/how-to-install-configure-and-enable-ssh-service-in-linux/
