Joomla is one of the oldest open sources and PHP based framework which allows the
users to build websites with a full Content Management System
(CMS). Joomla claims that they have around 2 million active
websites over the internet worldwide, which definitely means that
Joomla is actually a giant content management system (CMS). To
build your website, you can install Joomla on your Ubuntu Linux.
It’s really very simple and easy to use Joomla, and you don’t need
to know any HTML or CSS. [1][2]
Joomla on Ubuntu
Linux
The Joomla CMS can be installed through a web server. In this
case, as we are using the Ubuntu operating system, so we will be
using the Apache server to host the Joomla website. There are
options in your hand, you can either directly install the Apache
server on Ubuntu, or you can install the Xampp server inside your machine then
active the Apache server from the Xampp service. Today we are going
to learn how to install Joomla on Ubuntu. As we are dealing with
Ubuntu, so using the Apache server directly will be the best
option.[3]
Step 1: Get the Ubuntu System
Updated
As we are going to install the Apache server[4]
and PHP on our Ubuntu machine, so it’s very much important to keep
our machine up to date. This will get you the latest security patch
and repository.
$ sudo apt update -y && sudo apt upgrade -y
You can also use the Ubuntu ‘Software & Update’ to check whether
there is any update available or not.
$ sudo apt update -y $ sudo apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Get Apache and PHP on
Ubuntu Linux
PHP language is mostly configurable and compatible with web
servers and platforms. As we are going to install the Joomla on
Ubuntu, so we are am going to install PHP and Apache server on our
Ubuntu machine. If your machine doesn’t have the Curl
installed, you need to install the Curl first. The Curl is a
repository grabber form weblink. It will grab the PHP installer
files on Ubuntu.
$ sudo apt install curl
Now you can get the PHP repository installed on your Ubuntu
machine.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Now use the following terminal command line to get PHP and
Apache server. Then you can check whether PHP is installed on your
machine or not, by checking the PHP version.
$ sudo apt install apache2 libapache2-mod-php7.2 openssl php-imagick php7.2-common php7.2-curl php7.2-gd php7.2-imap php7.2-intl php7.2-json php7.2-ldap php7.2-mbstring php7.2-mysql php7.2-pgsql php-smbclient php-ssh2 php7.2-sqlite3 php7.2-xml php7.2-zip
If everything is done perfectly, you will get your Apache server
activated. Normally the Apache server is found under the localhost
address. You can check your Apache server address with the basic
net tool commands. In this case the ifconfig terminal
command can find the localhost IP address.
$ php -v
Once you are done installing the Apache server, now it’s time to
do some primary settings for the Apache server. Use these following
terminal commands to start, enable, and check the status of your
Apache server.
$ sudo systemctl start apache2 $ sudo systemctl enable apache2
Now you can check the status of the Apache server with the
systemctl command from the terminal on Ubuntu.
sudo systemctl status apache2

Step 3: Installing MariaDB for
Joomla
The Joomla requires at least one database language[5]
to interact with the Joomla database, and as we are going the use
the MySQL database, so we have to install and configure the MariaDB
on our Ubuntu machine. Then we will also be creating a specific
database for Joomla. Although, once the Joomla is installed on
ubuntu, we can change the database if we need it. But for now,
MariaDB is fine.
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server
After installing the MariaDB, we can now get inside the root of
the database for further security settings. We can change the
database password, grand any other user, associate with the Apache
server from the MariaDB settings.
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
Now we have to create a database for Joomla in MySQL. We will be
using the basic database commands to create and set the database.
After the database creating is done, we need to flush the settings
then exit from the database.
$ sudo mysql -u root -p CREATE DATABASE joomla_db; GRANT ALL ON joomla_db.* TO 'ubuntupit'@localhost IDENTIFIED BY '1234'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;

You can check the database that you just created form the
terminal command-line interface.
sudo mysql -u root -p show databases;

Step 4: Downloading Joomla on
Ubuntu Linux
Here comes the main part of this post, installing the Joomla
itself on the Ubuntu machine. We will be using the
wget command to download the compressed version of
Joomla, and next, we will unzip it inside the Joomla directory on
Ubuntu.
$ sudo wget https://downloads.joomla.org/cms/joomla3/3-9-16/Joomla_3-9-16-Stable-Full_Package.zip
After the download is finished, now we have to create a
directory for Joomla to be unzipped.
$ sudo mkdir /var/www/html/joomla

Before you start extracting the downloaded zip[6] file of the Joomla, let
me tell you, you might get an error of unable to get root access.
Even if you log in as a root user in the terminal, you may face
that problem anyway. To get rid of that problem, all you need to do
is just change the ownership of that folder from root to your
current user. You can use the chown command in the
terminal.
$ sudo chown jahid -v /var/www/html/joomla
Now you can unzip the Joomla zip file inside the desired folder.
You must remember the directory where the Joomla is being unzipped.
Because later, we will need that file path.
$ sudo unzip Joomla_3-19-16-Stable-Full_Package.zip -d /var/www/html/joomla $ sudo unzip Joomla_3-9-4-Stable-Full_Package.zip
Now I assume, downloading and extracting Joomla is done so far.
Now we have to configure the Joomla settings for our local usages.
We will be using either the Vim or Nano text editor to edit the
Joomla configure file on Ubuntu.
If you don’t have the Vim installed inside your machine, simply
install it from the terminal command line.
$ sudo apt install vim
Now open up the joomla.conf file with the editor
and add the following settings inside the configuration file. Then
save and close the file.
$ sudo vim /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf
Again, if you cant access the joomla.con file from
the terminal, you might need to change the root permission too of
those files.
$ sudo su $ sudo chown jahid -v /etc/apache2 $ sudo chown jahid -v /etc/apache2/sites-available/.joomla.conf.swp
Now you can unzip the Joomla package inside the desired
directory with full access.
$ sudo unzip Joomla_3.19-16-Stable-Full_package.zip -d /var/www/html/joomla
You might need to change the root administrator access to edit
the Joomla setting script.
$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/joomla $ sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/joomla
Use the systemctl command to restart the
Apache server system.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
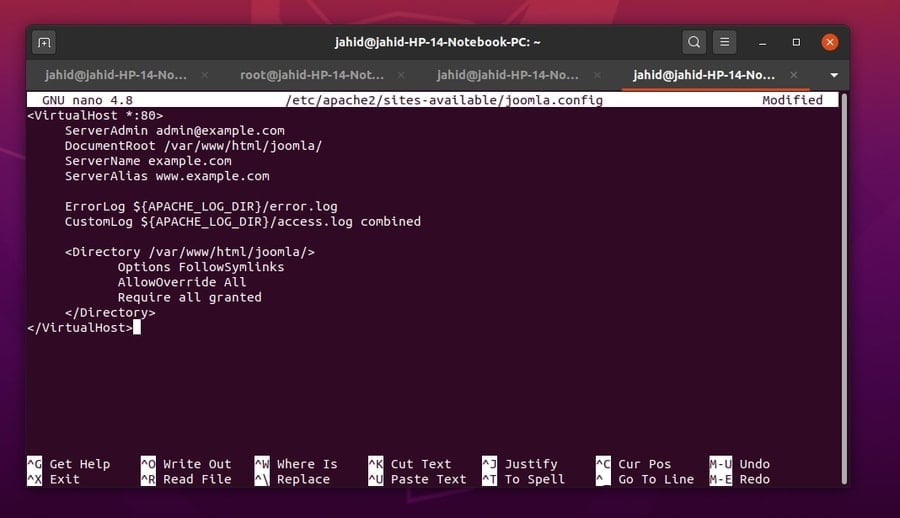
To configure the Joomla server, you can use the Vim or the Nano
editor. Open the Joomla.conf file in Nano editor. Now you have to
add the following configuration settings inside the .conf file. Now
save it and exit the file.
$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/joomla.conf
Now copy and pest the script settings inside your Joomla
configuration file with the Nano Editor.
VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin [email protected]
[7] DocumentRoot /var/www/html/joomla/
ServerName example.com ServerAlias www.example.com ErrorLog
${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log
combined <Directory /var/www/html/joomla/> Options
FollowSymlinks AllowOverride All Require all granted
</Directory> </VirtualHost>
Now to active and allow your host files to get the Apache
settings, run the a2enmod Apache script commands on
your Ubuntu machine.
$ sudo a2ensite joomla.conf $ sudo a2enmod rewrite
Finally, I hope you have done all the settings and
configurations correctly until now. By this, your system might get
the Joomla installed and enabled. Now you should reload your Apache
server and allow the Apache setting script to be rewritten. Then,
restart your Apache server again.
$ systemctl reload apache2 $ systemctl reload apache2 $ sudo a2enmod rewrite $ systemctl restart apache2 $ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 5: Getting Access from the
Firewall Settings
As we have installed a server and a database inside our Ubuntu
machine, it’s necessary to get the proper firewall access[8]
so that our site won’t get blocked by the internal network security
system. We will be using the uncomplicated firewall
ufw commands to check, enable, and disable the
firewall settings.
$ sudo ufw enable $ sudo ufw status
If you know the HTTP address and port of your website, you can
make a specific security clearance from the firewall settings.
$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
And, in the same way, to deny the firewall access for any
website use the following command lines.
$ sudo ufw deny 56/tcp $ sudo ufw allow from 192.168.0.1
To allow all the HTTP sites, use this command line in your
Ubuntu terminal line.
$ sudo ufw allow http
Step 6: Getting started with
Joomla on Ubuntu Linux
Here you go, now once the localhost webpage of the Apache server
is opened in your web browser, just add a forward slash
/ and add Joomla then hit the Enter button. If
everything is done, you should get the Joomla login page. Create an
ID with email and other credentials. Here you can change the PHP
version you need and change the SQL engine if you need it. But I am
going to leave them as default.
Now, after all the settings are done, you need to delete the
temporary installation folder of Joomla. Once you have deleted the
folder, you will be redirected to the Joomla login page. Use your
credentials and login to the Joomla CMS. Here you go, your Joomla
is ready to be used.

Once you have got access to the Joomla login page, you can
choose all the settings from the web login interface page. The
settings are very much easy to set up. Here you can choose the name
of your website, username, database type, and other settings. Once
you are done, you will get the option to delete the dummy
database/installation folder. Then you will automatically be
redirected to the login page again.
 This is the
This is the
Joomla site administrator page, where you will be asked your
username and password to enter inside the site.

Don’t forget to check your .htaccess file from the
Apache server folder, if you find any kind of problem to reach the
login page. Normally it takes ten minutes to get the Joomla
started. If it takes more than that, check inside your PHP
configuration setting file. You need to change execution time and
the memory limit settings from the PHP runtime configuration file.
The file must be named as php.ini. Open that file with Nano or Vim
editor, then enter the following script settings inside the
phprc file.
max_execution_time = 3000 ; memory_limit=128M ;
Final Thoughts
This post is all about how to get started with Joomla on Ubuntu
Linux. At the end of this post, I would like to remind you of some
common mistakes that you might do. Be careful while you unzip the
Joomla files and configure the settings. Change your Ubuntu user
root permission if requires. And one more thing, if you’re using
the Skype application on the same Ubuntu machine, make sure that
the network port of the Skype and the Apache server is not the
same. By default, Skype sometimes blocks the Apache server
port.
I have tried to make all the installation and configuration
processes clear to everyone. And, all the steps are described with
corresponding images for better understanding. I hope you find this
post useful and informative. If you are already a Joomla user, you
can share your experiences with us. Write your comments in the
comment section and also share this post on your social media so
that others can also learn about Joomla.
References
- ^
The 20
Best PHP Frameworks for Modern Developers in 2020
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Open
Source CMS: 25 Best Content Management System Tools
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Xampp
(www.apachefriends.org) - ^
Apache
server (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Top 15
Best Database Management Systems for Linux in 2020
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
How to
Zip and Unzip Files on Ubuntu Linux: An Ultimate Guide
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
[email protected]
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
The 15+
Linux Firewall Software For Protecting Your Linux System
(www.ubuntupit.com)
Read more https://www.ubuntupit.com/how-to-install-joomla-on-ubuntu-linux-an-complete-guideline/