Random Access Memory (RAM) is the central memory unit of a
computer system. RAM can process data randomly within a short
period of time. RAM is capable of modifying, extract, or store data
for a short time. That’s why most often, the RAM is also called the
temporary storage device. In a modern computer, RAM is the speedy
memory cheap that holds data and log files during the process of
completing one complete CPU cycle. In some cases, when the RAM
size is inadequate than the processor, the total system can get
slower until the RAM gets free. In Linux, besides using a SWAP
area, you can also write log files in RAM instead of the storage
device. Writing log files in RAM using Log2ram in Linux can make
your system faster and efficient. [1]
Working Mechanism of Log Files in
Linux
In computing, the term log file indicates the record of the work
schedules done by the computer. The log files are usually stored in
the /var/log/ directory in Linux. In the beginning,
the Log2ram was created for the Raspberry Pi boards[2]. The Log2ram system
helped the Pi boards to provide better performance.
We can also use the Log2ram method in Linux. In modern
computers, when some tasks are initiated, the log files are stored
inside the RAM for a few moments so that they can be synchronized
with the processor.
RAM is built with capacitors and resistors. The capacitor holds
and releases the electric charges that work as 0 and 1. We know
that computers also have cache memory to speed up the processor.
Most of the Linux users create a SWAP area to use that as an
extended virtual RAM. But let me tell you that there are
differences between the SWAP area and the Log2ram. In this post, we
will learn how to write log files in RAM using Log2ram in
Linux.
Step 1: Installing Log2ram in
Linux
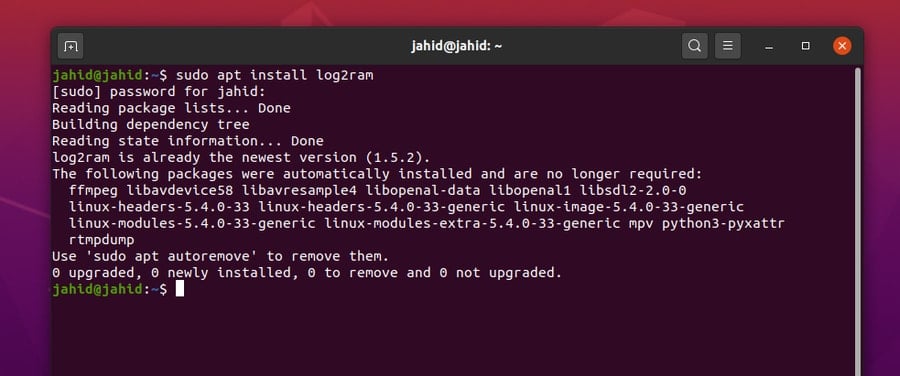
Installing the Log2ram tool in Linux is a straightforward
process. I will go through the entire process step by step. To
install Log2ram on your Linux system, first, update the system
repository. Then you can start with downloading the package and
store it inside the Linux filesystem[3].
You may proceed with echo and sudo
commands at a time to install Log2ram in Linux. Then, use the
wget terminal command to add a repository key.
Finally, run the apt install command in the terminal
shell to install the Log2ram in Linux.
$ sudo apt update $ echo "deb http://packages.azlux.fr/debian/ buster main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/azlux.list $ wget -qO - https://azlux.fr/repo.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add - $ sudo apt install log2ram
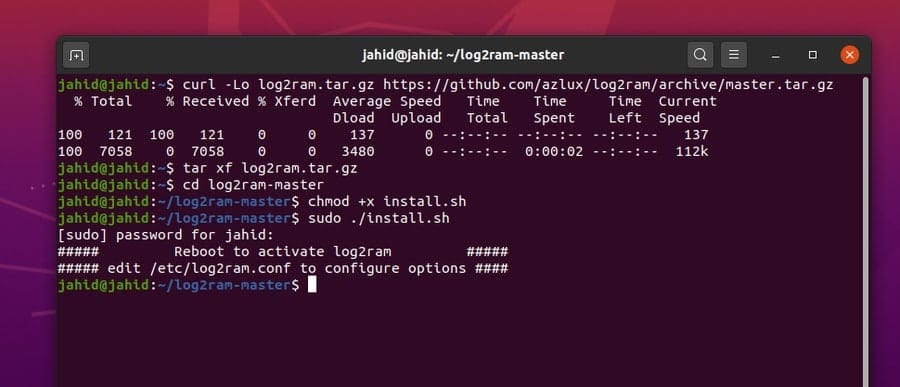
Here is an alternative way to install the Log2ram tool in Linux.
Here I am going to use the cURL command lines to
download the Log2ram tool. Then I will unzip and install Log2ram on
Linux. If your machine doesn’t have the cURL software installed,
you can install the Curl form here.
$ sudo apt install curl $ curl -Lo log2ram.tar.gz https://github.com/azlux/log2ram/archive/master.tar.gz $ tar xf log2ram.tar.gz $ cd log2ram-master
Once the download and installation are finished, run these
terminal command lines to take the Linux ownership, it will give
you full access to the filesystem and hardware. Now run the install
script to install the Log2ram on Linux.
$ chmod +x install.sh $ sudo ./install.sh
Step 2: Updating Log2ram in
Linux
Once you are done installing the Log2ram on Linux, you may need
to update and upgrade the Log2ram system. As the storage of a RAM
is not very much enough to store all log files, so you need to
update the Log2ram configurations frequently.
But unfortunately, there is no easy method to update or upgrade
the Log2ram tool by some terminal command lines. You need to stop
the Log2ram service and start installing the entire process again.
After you have done updating, never forget to reload the Log2ram
system and reboot the Linux machine.
$ sudo systemctl stop log2ram $ systemctl reload log2ram
Step 3: Mounting Log2ram in
Linux
In this step, we will learn how and where to mount the Log2ram
services. Usually, the log files are stored in the
/var/log directory in Linux. But as we are using the
Log2ram method, we need to assign a new directory to mount the
service.
We can also do a little configuration of Log2ram service through
the Nano or Vim script editor. The daily log files are written and
stored in the /etc.cron.daily/log2ram directory. On
the other hand, all Log2ram data logs are stored in
/var/log/log2ram.log.
$ sudo nano /etc/cron.daily/log2ram $ sudo nano /var/log/log2ram.log $ sudo df -h $ sudo mount
Step 4: Getting Started With
Log2ram
After installing and configuring the Log2ram service in Linux,
here come some handy and useful terminal command lines to operate
and monitor the RAM log files. We can see inside the log file,
check the system log list[4], and over-write
configurations through the terminal command lines.
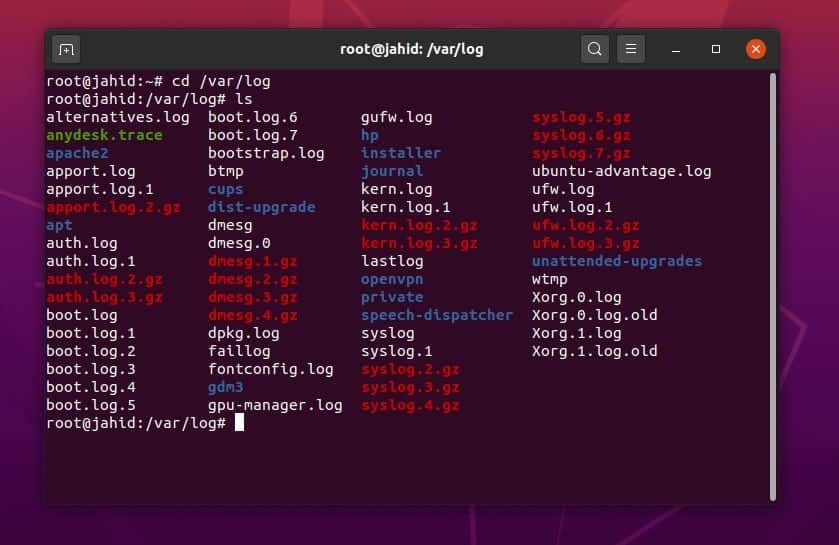
$ cd /var/log $ ls $ ls -l syslog* $ cd /var/log $ ls | wc -l
Here are some primary terminal command lines to read Log2ram
messages and create new Log2ram files on Linux. We can either use
the cat command or the tail command to
read log files. If any error occurs inside the Log2ram settings, we
can monitor it and fix it through the grep terminal command[5]. I am also adding some
primary Log2ram terminal commands to start, stop, and write files
on RAM in Linux.
$ less /var/log/messages $ more -f /var/log/messages $ cat /var/log/messages $ tail -f /var/log/messages $ grep -i error /var/log/messages $ sudo log2ram start $ sudo log2ram stop $ sudo log2ram write
Removing Log2ram from
Linux
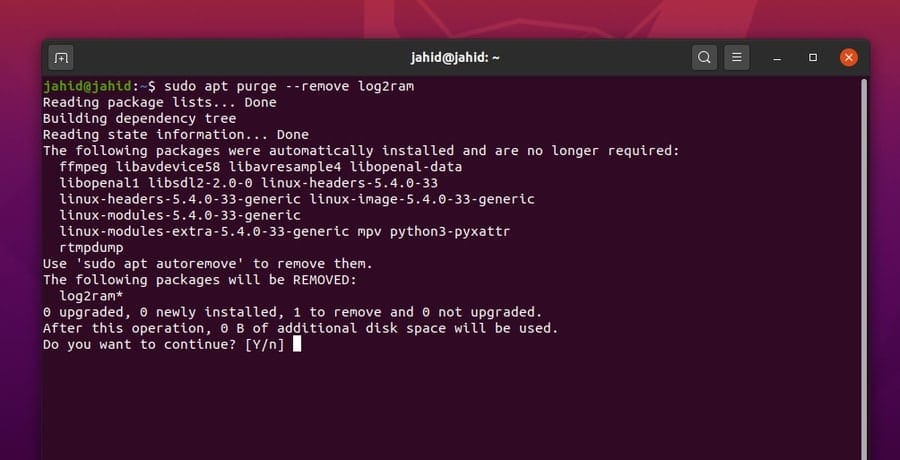
As I have mentioned previously, if you ever need to update the
Log2ram service in Linux, you will have to remove the complete
service. Then reboot the machine and start over the entire process
again. Here are some basic and primary terminal shell commands that
will help you to uninstall the Log2ram service in Linux. Also,
don’t forget to delete the configuration directory.
$ sudo apt purge --remove log2ram $ chmod +x /usr/local/bin/uninstall-log2ram.sh $ sudo /usr/local/bin/uninstall-log2ram.sh $ cd .. $ rm -r log2ram-master $ sudo reboot
Final Thoughts
Whatever service you are using to make your Linux system more
efficient, make sure that it is suitable for you. Otherwise, the
service itself will grab a lot of RAM. In this post, I have tried
to describe the method of installing and demonstrating some Log2ram
features on Linux. Definitely, by enabling the Log2ram service in
Linux, your physical memory will start working more efficiently,
and you will see significant improvement in performance. But be
mindful that a low capacity of RAM can slow down the entire process
of the computer.
So, hey guys, if you find this post useful and practical to
speed up your Linux system[6], share this post on your
social media. We also encourage you to write your opinions
regarding this post in the comment section.
References
- ^
CPU
cycle (www.oxfordreference.com) - ^
Top 20
Best Raspberry Pi Projects That You Can Start Right Now
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Everything You Need To Know About the
Linux File System (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
check
the system log list (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
50
Productive and Practical grep Command for Linux Enthusiasts
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
How To
Speed Up Ubuntu Linux: 12 Must Follow Tips
(www.ubuntupit.com)
Read more https://www.ubuntupit.com/how-to-write-log-files-in-ram-using-log2ram-in-linux/