The increased use of information technology in our everyday life
and business has led to cyber-attacks becoming more sophisticated
and large-scale. For organizations to thrive in this era of
technology, they must develop robust security strategies to detect
and mitigate attacks. Defense in depth is a strategy in which
companies use multiple layers of security measures to safeguard
assets. A well-implemented defense in depth can help organizations
prevent and mitigate ongoing attacks.
Defense in depth uses various cutting-edge security tools to
safeguard a business’s endpoints, data, applications, and networks.
The objective is to prevent cyber threats, but a robust
defense-in-depth approach also thwarts ongoing attacks and prevents
further damage.
How organizations can implement defense in depth
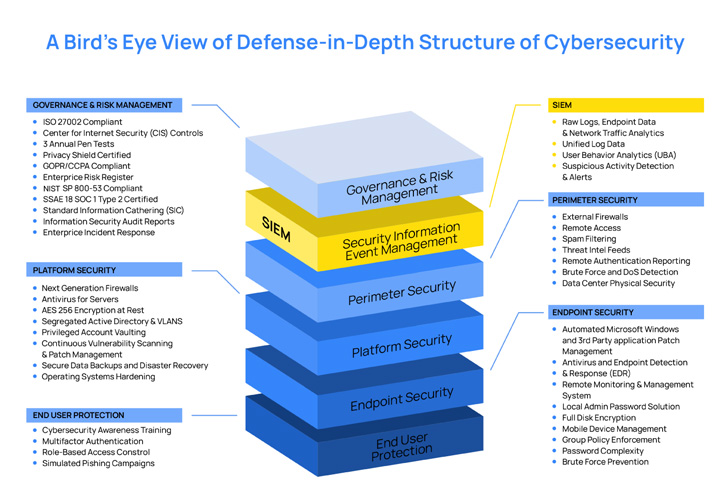 |
| The image above shows the various layers of security that organizations must implement. Below we describe ideas that companies should consider for each layer. |
Governance and risk management
Governance and risk management in cybersecurity revolves around
three major elements; governance, risk, and compliance (GRC). The
overarching purpose of GRC is to ensure that every member of an
organization works together to achieve set targets. They must do
this while adhering to legal and ethical guidelines, processes, and
compliance standards. Such standards include NIST, PCI-DSS, HIPAA,
and GDPR. Establishments must identify the standards that apply to
them and use tools to automate and simplify the compliance process.
These tools should be able to detect violations and provide reports
and easy-to-follow documentation to resolve the violations.
Platform security
There are many ways organizations can ensure the security of the
devices in their enterprise network. Two essential methods are
vulnerability management and operating system hardening.
Vulnerability management adds a layer of protection that ensures
that companies address weaknesses in software before attackers can
exploit them. On the other hand, OS hardening ensures that security
teams implement additional measures to protect the integrity of
data and configurations used in an operating system. They can do
this by defining and enforcing policies for endpoints in their
network. Other elements to ensure platform security are firewalls
and implementing appropriate network segmentation.
SIEM
A security information and event management (SIEM) solution is
essential to an organization’s security strategy. A SIEM aggregates
and correlates logs from different sources and generates alerts
based on detection rules. It also provides a central management
portal for triaging and investigating incidents, and being able to
collect and normalize logs from different tools and systems is one
of the essential features of a good SIEM.
Perimeter security (threat intelligence)
Successful implementation of defense in depth is not focused
only on the organization’s internal infrastructure but also on
threat actor activities. Institutions must have a way of gathering
and analyzing threat intelligence and using the data to provide
security for their assets. Security teams must also use firewalls
and network segmentation to protect critical infrastructure.
Endpoint security
The endpoints in an organization are critical to its operations,
especially in the 21st century. Endpoint security is vital because
attackers usually seek to compromise data stored on endpoints.
Endpoint security has evolved over the years from anti-virus
solutions to full-blown antimalware solutions, and now we are in
the era of extended detection and response (XDR) solutions. XDRs go
beyond the limitations of traditional antimalware solutions by
correlating alerts from various sources to provide more accurate
detections. They also leverage SIEM and SOAR (Security
Orchestration, Automation, and Response) functionalities to detect
threats in multiple endpoints and respond uniformly and effectively
to any compromised endpoints.
Wazuh, the free and open source solution
Wazuh[1] is a free, open source
security platform that offers unified SIEM and XDR protection. It
protects workloads across on-premises, virtualized, containerized,
and cloud-based environments. Wazuh provides support to security
operations with easy integration to threat intelligence feeds.
In implementing defense in depth, no single tool can cover all
layers of security. However, Wazuh offers many features that
organizations can use to strengthen their security infrastructure.
For GRC, Wazuh provides dedicated dashboards that monitor and
investigate events triggered by PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR
violations. The solution also has a vulnerability detector module
with out-of-the-box integration with vulnerability feeds, which
scans operating systems and applications for known
vulnerabilities.
Wazuh also provides a Security Configuration Assessment (SCA)
module that enables users to create policies that the Wazuh server
applies to every endpoint in their environment. Companies can use
vulnerability detector and SCA modules to strengthen the security
of the operating systems and applications deployed on their
endpoints.
As an XDR, Wazuh correlates security data from several sources
to detect threats in an organization’s environment. Also, it can
actively mitigate threats by using its active response
capability.
Wazuh is one of the fastest-growing open source security
solutions, with over 10 million downloads per year. Wazuh also
provides communities[2]
where users can engage Wazuh developers, share experiences, and ask
questions related to the platform. Check out this documentation[3]
on how to get started with Wazuh.
References
- ^
Wazuh
(wazuh.com) - ^
communities
(wazuh.com) - ^
documentation
(documentation.wazuh.com)
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/10/implementing-defense-in-depth-to.html
