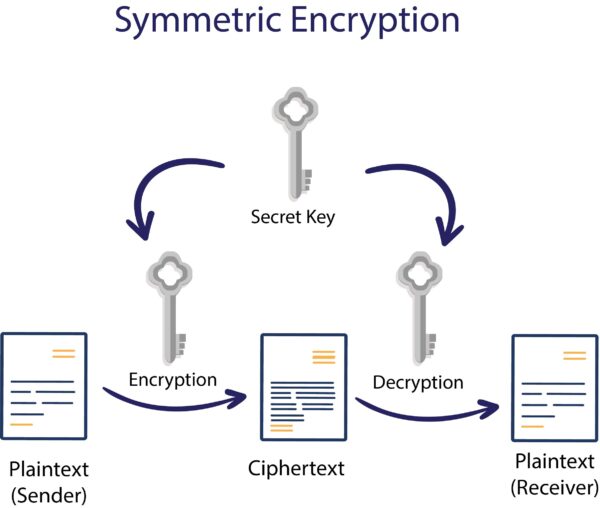
A key management protocol is a set of rules and procedures used to handle cryptographic keys in a secure and efficient manner. These protocols are essential for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data in various cryptographic systems. There are several key management protocols used in different contexts. Here are a few notable ones:
- Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP): KMIP is an OASIS standard that defines a single, comprehensive protocol for the management of cryptographic keys and related objects. It allows for interoperable communication between key management clients and servers, supporting a wide range of encryption systems.
- Internet Key Exchange (IKE): IKE is a protocol used to establish and manage security associations (SA) and cryptographic keys for secure communication in IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) VPNs. It is part of the IPsec suite and helps to establish secure connections between network devices.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) Handshake Protocol: TLS is a cryptographic protocol used to secure communication over a computer network, such as the internet. The TLS handshake protocol helps in the exchange of cryptographic parameters and the establishment of session keys for secure data transfer.
- Secure Shell (SSH) Key Management: SSH is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure remote access and data transfer. SSH key management involves generating, distributing, and using public and private key pairs for authentication and secure access to remote systems.
- Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP): SCEP is a protocol used for the enrollment of digital certificates, including public and private keys, onto network devices. It simplifies the certificate enrollment process and is commonly used in Public Key Infrastructures (PKI).
- Key Agreement Protocols: These are protocols that allow two or more parties to establish a shared secret key securely over an insecure communication channel. Examples include Diffie-Hellman key exchange and Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) key exchange.
These are just a few examples of key management protocols used in different security and cryptographic applications. The specific protocol used depends on the context and the cryptographic system being employed. Each protocol has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of the appropriate protocol depends on the security requirements and compatibility with the systems involved.