As businesses continue to grow, they are likely to look for a
cost-effective solution for managing their tech infrastructure. One
of the best selling points of using Linux for business is that it
is entirely open-source. This means less payment to proprietary
software vendors and the availability of a large community of
active developers. Moreover, Linux has all the things needed for
running, even the largest of enterprises. Plus, most of the things
that run on Linux are completely free of charge. You will be only
paying for enterprise tech supports if you want to get such
services.
No matter what type of business you are running, Linux has all
the applications you need for your day to day operations. We have
compiled an extensive set of software that one may find useful when
migrating from a non-Unix tech stack to a Linux and BSD setup.
Please bookmark this guide for future references and use the tools
that are required for your business.
1. Best Linux Distros for
Business
Systems that leverage the Linux kernel are known as
distributions. There is a wide
range of distributions[1]
that you can choose for your business. We are outlining some
general-purpose desktop and Linux
server distributions[2]
that you might be interested in. We will also be highlighting some
popular Linux desktop environments for people who need a GUI
setup.

Ubuntu
Ubuntu is the most popular Linux distro for both personal
computers and server workstations. It is a solid OS that offers an
excellent feature set without any charge. Plus, you get to use a
large number of exciting software without having to worry about
running out of support. If you want to use Ubuntu as your company server[3], don’t forget to check
out their Pricing plans.
Debian
Debian is another very popular Linux OS that you can use for
powering your next business. It is extremely feature-rich and is
much more stable than many traditional distros. In fact, Ubuntu
itself is built on top of Debian. One key benefit of Debian is that
it runs on most hardware and thus makes itself a good choice for
companies that still utilize legacy hardware.
Arch
Arch Linux is arguably one of the most powerful Linux distros of
all time. It provides extreme control over the system and has very
good documentation. Thus, it is very easy to get started. The
Pacman utility and AUR make package management fast and simple
while rolling out cutting-edge applications every now and then. It
is particularly a great choice for companies that retain skilled
sysadmins in their ranks.
RHEL
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux or RHEL is a solid distro aimed at
companies that use Linux for businesses. It is a suitable choice
for running bare metal servers, IaaS, containerized services as
well as standard desktop workstations. Since RHEL is built
specifically for serving businesses, enterprises can choose from a
number of feasible pricing options.
CentOS
CentOS is a community built alternative for RHEL. It has got all
the features needed by modern businesses and is generally very
stable. A lot of companies use CentOS for powering enterprise
servers. Thus, if you want to try a Linux distro with a solid
feature set but free of charge, CentOS could be a good start.
The above mentioned Linux distros can be used with or without a
graphical user interface. This should be the case if you are using
them for running your servers. However, if you want to use Linux
for business workstations, your employees may want to use a GUI.
Below are some of the best
Linux desktop environments that provide this graphical support.
[4]
GNOME
The GNOME desktop is one of the most popular desktop
environments for Linux, and for good reasons. It offers an elegant
interface for interacting with your system without draining
excessive CPU resources. Many popular distros use GNOME as their
default desktop environment, including Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and
CentOS.
KDE Plasma
KDE Plasma is a gorgeous
looking GUI[5] with support for extreme
customization. It looks very beautiful and is easy to use. KDE
applications are well supported and roll out new releases pretty
often. However, KDE is known for consuming too much CPU resources.
Thus, it would not be an ideal choice for older PCs.
XFCE
XFCE is a very lightweight desktop
environment that runs smoothly even on older hardware. It does so
by cutting on the appearance section and provides a minimal looking
GUI. However, it is very fast and is regarded very highly by most
Linux users due to its efficiency and speed. [6]
2. Communication
Effective communication is crucial for the success of your
enterprise. Below, we are outlining some useful apps that may come
in handy for companies who are using Linux for business. These
include tools like email servers, clients, VoIP, text, and instant
messaging apps.
Email servers are software that is responsible for the transfer
of emails from one server to another. They are divided into mail
transfer agents(MTA) and mail delivery agents(MDA). Check out
our guide on Linux email servers[7] for detailed information
on all available options.
Exim
Exim is a powerful MTA that is suitable for powering scalable
email servers. It is a command-line tool written using C and thus
offers excellent performance.
Postfix
Postfix is a popular mail transfer agent that is used by a large
number of institutions due to its rich feature set and solid
performance. It is free software, so you can use it exclusively
without emptying your budget.

Dovecot
Dovecot is a robust mail delivery agent for Linux and BSD
servers. It provides a lightweight and simple to use mail service.
One key feature of Dovecot is that it is highly secure and thus
isn’t prone to server attacks.
Sendmail
Sendmail is a solid email routing framework that is widely used
for powering enterprise email servers. It is feature-rich and very
secure, thus making it a viable choice for a lot of businesses.
Moreover, you will get top-notch customer support from its
vendor.
Email clients or mail user agents are computer applications that
allow users to retrieve their mail communications. There are many
open-source Linux email clients[8] you can use for your
business.
Mailspring
Mailspring is a robust email client with a
rich set of features. It is cross-platform and thus runs across all
major computer platforms. This makes it a good choice for
corporations that use several operating systems across their
infrastructure. [9]
Geary
Geary[10] is a lightweight and
fast email client with a sleek looking user interface. It is
written using the Vala programming language and is adopted by
Canonical for the Ubuntu distribution. Geary is now being
maintained by The GNOME Project.
Thunderbird
Thunderbird is an extremely powerful email client developed by
the Mozilla Foundation and released as open-source software. It
also works as a chat client, RSS, and news feed. Thunderbird also
supports a large number of add-ons that increase its
functionality.
Evolution
Evolution is an old but powerful email client for Linux that is
a worthy alternative to Microsoft’s Outlook program. It offers an
intuitive information management system, which makes it a good
choice for businesses powered by Linux.
Instant messaging has become very popular over the last decade.
It allows users to communicate in real-time. So, if you want to use
Linux for business, instant messaging apps[11] can be a great way for
hassle-free communication among team members.
Discord
Discord is a very popular instant messaging app that allows
members to communicate using text, image, audio, and video
communication. Although it is a proprietary solution, Discord has a
free version that can be used by anyone. Moreover, the Discord app
for Linux is very intuitive and easy to use.
Telegram
Telegram is an open-source IM app that can be used for instant
messaging as well as voice over IP communication. It provides
clients for Linux[12], Mac, Windows, iOS, and
Android. So, if you are looking for an IM app that can be accessed
from any platform, Telegram seems to be a good choice.
Viber
Viber is arguably one of the most popular IMs among millennials.
It offers some notable features, such as syncing among multiple
devices as well as platforms. You can use it for text, audio, and
video communication, which makes it a viable solution for
enterprise teams.
Signal
Signal is a safe instant messaging platform that provides
end-to-end encryption support for all your communication. Many
large businesses use Signal for maintaining team communication for
this reason. Check out our
earlier guide on Signal to learn how to install it on Linux.
[13]
Video conferencing has become a staple of effective business
communication. Companies all over the world use this service on a
daily basis. There are many solid
video conferencing software for Linux[14] you can use.
Skype
Skype is one of the most popular video conferencing solutions
worldwide. One major advantage of using Skype is that it runs on
all major platforms alongside Linux. This means employees from any
device or platform can use Skype for business meetings or team
briefings.
Apache OpenMeetings
Apache OpenMeetings is a very powerful video conferencing app
written in Java. It is developed and maintained by the Apache
foundation. Employees can use OpenMeetings for giving online
training, business presentations, hosting whiteboard
collaborations, and desktop sharing as well as video
conferences.
Jitsi
Jitsi is another solid video conferencing solution for teams
that use Linux for business. It has an intuitive user interface
which is very easy to use. One key benefit of Jitsi is that
companies can use it for deploying personalized video conferencing
platforms.
3. Productivity
Productivity apps include tools that make your teams’ workflow
easier to manage and speed things ups. These applications include a
wide set of tools, ranging from notepads to time trackers. Below
are some essential tools that will help to maintain your workflow.
Check out our earlier guide on Linux
productivity software[15] for additional
information.
ClickUp
ClickUp[16] is an excellent
productivity booster app that offers features like to-do lists,
project management, spreadsheets, chats, docs, wikis, reminders,
and many more. Moreover, the cross-platform nature of the app makes
it accessible from any platform.
NATTT
NATTT[17] or Not Another Time
Tracking Tool is a simple but useful
time tracker app for Linux[18]. It is very easy to use
due to its intuitive user interface and simple workflow. All users
need to do is create a task and start tracking the time spent on
it. The usage statistics can be exported very easily.
Medleytext
Medleytext is a robust note-taking tool
aimed at programmers and developers. It allows people to create
simple yet expressive programming ideas or blogs using markdown.
Medleytext is also very easy to customize based on the user’s
preference. [19]
Project Brainstorm
Project Brainstorm[20] is a privacy-focused
note-taking app with features like note sharing, searchable tags,
syntax highlighting, server hosting, and so on. It is ideal for
teams who are looking for a secure and remotely accessible note
taker.
KeePassXC
KeePassXC[21] is a free yet powerful
password management tool for Linux[22]. It makes it easy to
set up strong passwords without having to remember them
individually. KeePassXC can work in offline and supports features
like automatic password fillups, password strength meter, easy
browser integration, database mergers as well as a CLI
frontend.
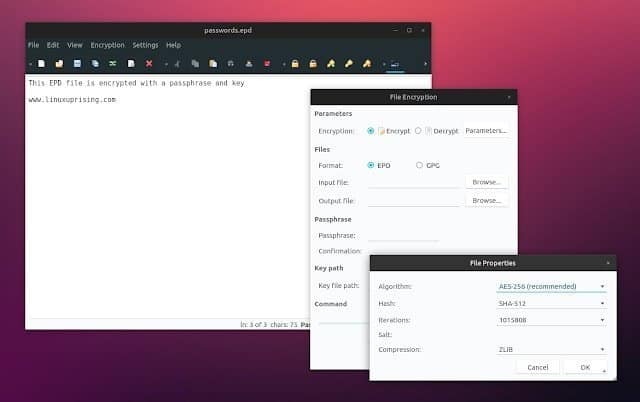
EncryptPad
EncryptPad[23] is a robust and
encrypted text editor for Linux users who take privacy seriously.
It is an ideal choice for companies who use Linux for business due
to its strong stance on security. It can work with both binary and
OpenPGP files and supports encryption algorithms like AES128,
AES256, SHA-256, SHA-512, and TripleDES.
Tomboy
Tomboy is an easy to use note-taking app for Linux developed by
the GNOME project. It is a suitable choice for teams that need
simple yet versatile notepads for brainstorming and organizing
their ideas. Tomboy supports several styling & sizing, bullet
lists, note synchronization, backup, and inline spell checking.
f.lux
f.lux is a modern-day Linux app that reduces strain to the eyes
of people who use their computers for a prolonged period. It
changes the color of the screen based on the current time. It is
readily available for Linux as well as Mac and Android.
Kontact
Kontact is a very powerful information manager developed by the
KDE project. It allows users to group their contacts, emails,
to-do’s, and calendars into a single unified screen. We highly
recommend Kontact to teams who are looking for a robust PIM
solution for Linux.
AutoKey
AutoKey is a free yet useful automation utility developed for
Linux and x11. It allows users to create frequently used phrases
that can be inserted using a single hotkey. This is useful for
opening programs as well as writing emails with trivial strings or
signature.
Catfish
Catfish is a versatile searching tool written using Python. It
utilizes the Linux find command in the background and allows users
to search for files from its GTK+ user interface.
Remmina
Remmina is a popular remote desktop client for Linux and other
POSIX-compliant systems. It is the default way of accessing a
remote desktop in Ubuntu and Debian. Remmina has pre-built support
for many communication protocols like RDP, VNC, NX, SPICE, and SSH.
Thus, it’s a great way of sharing desktop sessions[24] for enterprises that
use Linux for business.
4. Imaging and
Design
Linux offers a good number of tools for displaying and
manipulating images or video files. You can also choose from a
well-rounded set of design software, including tools for CAD design
and vector images. We are outlining some apps for these
purposes.
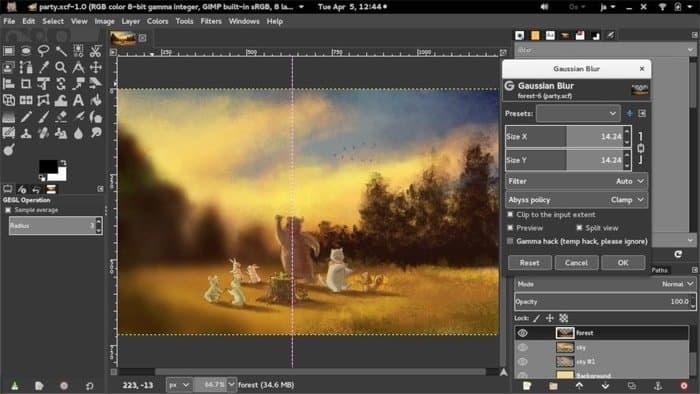
GIMP
GIMP[25] is a free yet versatile
image editing and manipulation tool. It is one of the most popular
Linux image editors due to its rich feature set and easy to use
user interface. It also allows users to edit raster graphics and
transcode images from one format to another.
ImageMagick
ImageMagick is a suite of imaging libraries that can be used for
creating, displaying, editing, modifying, and converting raster
images. It is one of the oldest and most stable image editing
software for Linux-based distros. Moreover, ImageMagick supports
well over 200 different image formats.
Inkscape
Inkscape[26] is a tool for creating
and editing vector graphics[27]. It generally works
with the Scalable Vector Graphics format but also allows users to
import/export other vector formats. Inkscape is totally open-source
and thus a good solution for companies that use Linux for
business.
Krita
Krita[28] is a free editor for
raster graphics images and can be used for creating digital
paintings as well as 2D animation. It offers an intuitive user
interface and supports features like dynamic brush tools, advanced
mirroring, and layer management.
Amide
Amide is a free but robust medical imaging software for Linux[29]. It provides features
like a powerful anisotropic filtering wizard, cropping support, and
drawing 3-D ROIs.
Aliza
Aliza is another medical imaging software that supports many
advanced features such as a powerful DICOM viewer and 2D, 3D, and
MPR rendering. It also provides features for ROI’s, overlays, DWI,
compression, and many more.
RawTherapee
RawTherapee is a powerful photo processor that can be used as
an
alternative to tools like Adobe Lightroom[30]. It offers a wide range
of useful features like floating-point processing, several
denoising methods, advanced color handling, and so on.

Calligra Flow
Calligra Flow is free diagramming software developed and
distributed by the KDE project. It is actually a suite of imaging
tools that include utilities for creating presentations, PDF
documents, vector drawings, and project management, among
others.
Avidemux
Avidemux is a free yet feature-rich video
editing software for Linux[31] and offers features
like video encoding, filtering, and cutting. It has a clean and
concise UI which makes Avidemux easy to use for companies that use
Linux for business
OpenShot Video Editor
OpenShot Video Editor is one of the most popular video editors
for Linux and BSD distributions[32]. The project aims to
provide an easy to use yet highly functional video editor. Since it
comes under the GNU GPL license, companies can easily explore the
source code.
KiCad
KiCad is arguably one of the best
electronic design automation tools for Linux[33]. It is an excellent
tool for creating PCB layouts, schematic capture, and Gerber files.
So, if you are an electronic manufacturer who wants to switch to
Linux for business, KiCad can be a viable alternative to your
existing EDA tools.
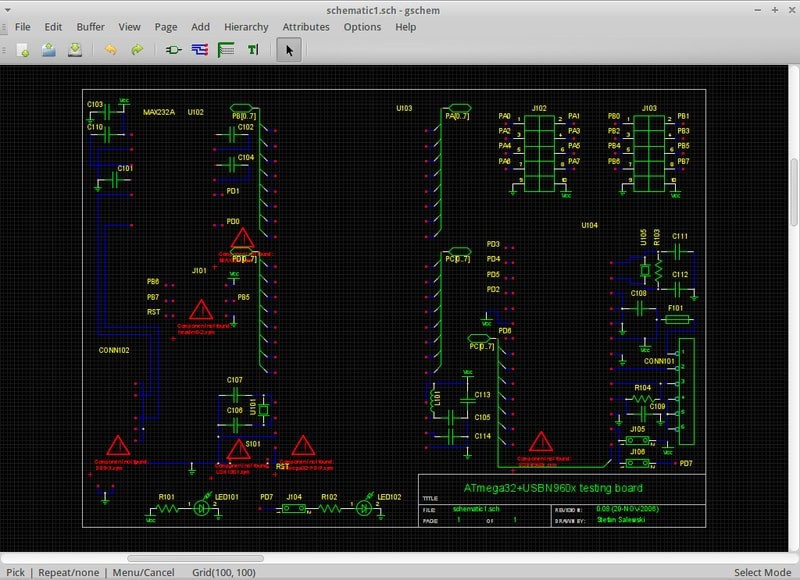
gEDA
gEDA is a framework of open-source EDA tools that allow
electronic design manufacturers to create high-quality PCB layouts
and robust schematics. Designers can use this solution for bulk
editing PCB layouts and streamline their chip designing
workflow.
Open Cascade
Open Cascade is a solid CAD implementation for Linux. It is an
excellent choice for companies who want to use Linux for business.
Open Cascade is written in C++ and thus provides a more than
optimal performance.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD[34] is a free yet versatile
CAD solution for Linux users. It can be a viable alternative to commercial CAD applications
like AutoCAD[35]. It provides a simple
to use Python API, which makes it easy to customize based on your
business requirements.
5. Content
Management
If content creation is your company’s primary service, you
should look at some essential tools that Linux offers. Below are
some useful apps and services that will come in handy for content
creation[36] as well as
management.
LibreOffice
LibreOffice[37] is a free but extremely
powerful office suite for Linux distributions. It is a worthy
alternative to Microsoft’s Office lineup and provides all the major
features required for modern businesses. LibreOffice has a clean
looking UI alongside advanced features like automatic spellchecks
and OpenPGP encryption.
FreeOffice
FreeOffice[38] is another free yet
feature-packed office suite for the Linux community. This office
application consists of three components. A word processor unit
called TextMaker, a spreadsheets and charts creator called
PlanMaker, and a presentation frontend named Presentations.
Joomla
Joomla[39] is a popular content
management system(CMS) written in PHP. It allows Linux users to
create, edit, and publish blogs as well as SEO optimized
content.
WordPress
WordPress is, without any doubt, one of the best CMS
applications ever. It is being used for powering a large number of
sites we see every day. Thus, the application is very well
maintained and provides top-notch performance.
KompoZer
KompoZer is an open-source WYSIWYG HTML editor that allows users
to design and publish high-quality web content. Although the
project has been abandoned for some time, it still enjoys relative
popularity among Linux-based content creators.
Textpattern
Textpattern is a simple and lightweight content management
system aimed at personal bloggers and hobbyists. It allows users to
write well-structured and easily maintainable blog posts.
Discourse
Discourse is a popular forum management solution[40] that runs effortlessly
on Linux. It allows companies who use Linux for business to manage
their online community without facing unwanted hassles. You can
also use Discourse as a mailing list or chat room.
miniBB
miniBB is a simple and lightweight forum software for Linux that
allows people to create a personalized forum in no time. The
software is very easy to use and provides a comfortable,
lightweight, and speedy way of building a personal web forum.
RedNotebook
RedNotebook[41] is a modern and
flexible journaling solution for Linux, which makes it very easy to
take personal notes or save personal diaries. It offers highly
customizable templates and supports features like calendar
navigation, word counter, and note exports.
6. Financial
Applications
Modern enterprises require sophisticated business tools[42] for managing their
growth. Linux offers many powerful applications that will help you
to migrate from your current platform to Linux. Below are some such
applications you can use for commercial reasons.
GnuCash
GnuCash is a solid
finance app for Linux[43] that offers excellent
accounting features. It provides a double-entry bookkeeping system
that can store all your company’s financial data very effectively.
Moreover, GnuCash is entirely free of charge and thus saves huge
money from your accounting budget.
KMyMoney
KMyMoney is another double-entry bookkeeping system that can be
used to store and track financial information at ease. The software
is developed by KDE and is thus free to use. KMyMoney makes assets
management easier by keeping individual track of stocks, bonds,
mutual funds, and supports well over 170 currencies as of now.
gretl
gretl is a free and open-source statistical library aimed to
provide econometrics support. It can use a wide range of
statistical methods on business data and make
sense of content to economic relationships[44]. Some of its noteworthy
features include support for parallelization, various time series,
machine learning, panel-data estimation, and a wide range of output
formats.
R Project for Statistical
Computing
The R project is one of the most popular means of performing
statistical estimation. It is used widely by businesses around the
world due to its superior feature set and active community support.
R is also enjoying a surge in popularity due to the recent increase
in data mining technologies.
openCRX
openCRX is an excellent CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
tool that allows companies to break the barrier between
organizations and their clients. It is a viable alternative to paid
platforms like Salesforce and Zoho. Some of its prominent features
include effective sales forecasting, reports, management,
ticketing, sales automation, and collaborative support.
Yetiforce
Yetiforce is another great
CRM solution for companies[45] that use Linux for
business. It is entirely free of cost, and the open-source codebase
is open for anyone who wants to explore. Yetiforce is a
GDPR-compliant solution with support for email marketing, lead
conversion, IT asset management, task automation, and real-time
support.
Zammad
Zammad is a prominent help desk software[46] that makes it easy for
companies to sort out customer queries as soon as possible. A lot
of companies use Zammad to stay connected to their clients for
providing top-notch business support. It supports many different
communication channels, including chat, social network, email, and
telephone.
OTRS
OTRS or Open Source Ticket Request System provides a
free and efficient way of managing client queries. It has an
intuitive web interface that is simple to use yet packs many
essential features. Some of its main features include standard
replies, ticket locking, auto-responding, and a personalized
templating mechanism.
7. Network and Server
Applications
Almost every major enterprises around the world use Linux for
business servers. There is an abundance of network and server
applications you can choose for powering your web infrastructure.
Below, we are outlining some of the essential tools for this
purpose.
Apache
The Apache
web server is one of the most widely used server applications
in the world. It is developed by the Apache Software Corporation
and is released as free software. Most websites use Apache for
serving web content like HTTP pages, files, scripts, and so on.
[47]
Nginx
Nginx[48] is another popular
Linux server application that enjoys widespread popularity. It is
often used as a proxy server or load balancer. It can handle
WebSockets, TLS/SSL with SNI, FastCGI, massive concurrent
connections, dynamic certificate loading, and so on.
Samba
Samba is a cross-platform implementation of the SMB protocol and
is used heavily for powering FTP servers. It offers a fast, stable,
and secure method of running file, print, and directory services
alongside many more.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN[49] is a commercial
application for building virtual private networks. It is essential
for any company that wants to build its tech stack on top of Linux.
Although OpenVPN is a proprietary solution, the codebase is
available freely.
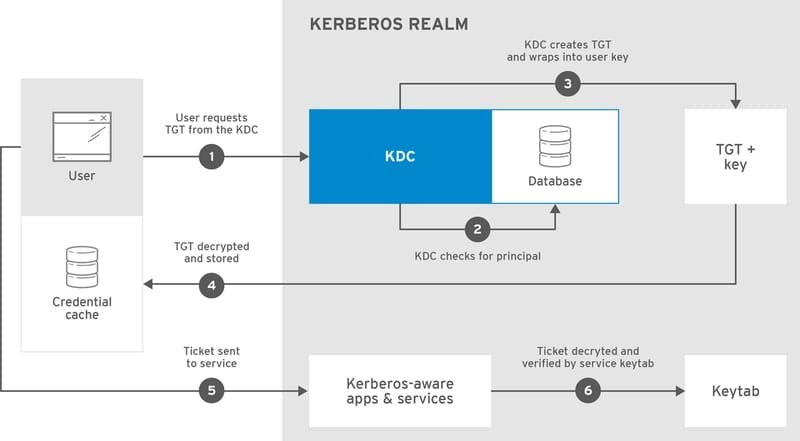
Kerberos
Kerberos is a network service authentication protocol that
provides client authentication based on a trusted third party
called Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC). It is widely used in
the tech industry due to its safe and efficient service.
MySQL
MySQL is arguable one of the most popular database management system for
Linux[50]. It is an open-source
solution that is generally used for data warehousing, e-commerce
businesses, and logging. Many popular blogging websites for Linux
use MySQL, such as WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL[51] is an extremely
powerful relational database suitable for building large scale
enterprise solutions. It offers features like nested transactions,
multi-version concurrency control (MVCC), table inheritance, and a
robust locking mechanism.
iptables
iptables is an extremely powerful packet filtering and routing
tool offered by Linux. It uses the Linux kernel’s Netfilter module
for creating filtering rules. Check out our guide on essential Linux iptables rules[52] to learn more about
this tool.
UFW
UFW[53] or Uncomplicated
Firewall is a simple yet robust firewall mechanism. It is the
default firewall of the popular Ubuntu distribution. It is
essentially a GUI wrapper around the iptables utility.
Metasploit
The Metasploit project is a powerful security framework[54] that allows ethical
hackers to find flaws in an enterprise network. It is arguable one
of the most popular open-source security tools for Linux.
Nmap
Nmap is a robust network scanner that can be sued for finding
entry points to business infrastructure. If you use Linux for
business, then you should be familiar with these essential Nmap commands[55]. They will help you
identify weak points in your server.
Kali Linux
Kali
Linux[56] is a standalone Linux
distribution that focuses on security. It comes packed with a large
set of security tools and is thus a good choice for penetration
testing.
netstat
netstat is a CLI-based monitoring tool for Linux[57] distributions that
offers information on active network connections and connection
statistics. It is a simple but versatile tool and is widely used by
sysadmins for monitoring their servers.
8. Backup and
Cloning
Enterprises need to deal with a massive amount of data, and they
need to do this securely. Creating regular backups is one of the
first rules of developing a disaster recovery plan. Here are some
essential Linux backup solutions[58] that may come in handy
for such requirements.
Bacula
Bacula Enterprise is an extremely powerful backup solution for
Linux. It is an open-source product but also offers a convenient
enterprise package for companies that use Linux for business. Check
out our
review of the Bacula Enterprise solution[59] to get a detailed
overview of that.
Amanda
Amanda is a multi-platform Network Disk Archiver that can be
used to take backups of multiple disk drives or computers. It is
built using a client-server model and can take scheduled backups
very easily.
Time Vault
Time Vault is a simple but useful software for taking
incremental snapshots of your Linux
file system[60]. It is inspired by
Apple’s Time Machine and offers features like an intuitive GUI
interface, versioned backups, automated snapshots, and so on.
Clonezilla
Clonezilla is, without any doubt, one of the best
disk cloning software for Linux distributions[61]. It comes in two
variants, Clonezilla Live and Clonezilla server. The live version
can clone only one system at a time, whereas the server variant can
clone up to 40 systems simultaneously.
GParted
GParted[62] is the most widely used
partition manager for Linux[63]. However, it also
offers features for disk cloning. Thus, admins can simply use
GParted to clone their system without having to install a new
cloning software altogether.
Mondo Rescue
Mondo Rescue is a solid disaster recovery solution that works on
Linux and FreeBSD. It is written in C, thus resulting in much
faster performance. You can use it to clone tapes, USB devices,
network, LVM, RAID systems, and many more.
Open Media Vault
Open Media Vault is a Debian-based NAS
(Network Attached Storage) solution for Linux[64]. It allows users to
clone or backup their data from an impressive web interface.
9. Virtualization and
Cloud
Virtualization allows companies to make effective use of their
computing resources. Linux offers multiple virtualization methods
and tools in this regard. Check out some essential applications
that are used widely for this purpose.
VMware Workstation for Linux
The VMware Workstation for Linux is a solid virtualization
offering from VMware, the company that made enterprise
virtualization prominent around the world. It allows users to run
multiple operating systems on a single host machine and thus gain
better isolation among services.
QEMU
QEMU is a popular hypervisor that provides OS-level
virtualization for Linux users. This allows sysadmins to run
non-Unix systems easily in their Linux machine. It is written using
C and thus offers better performance than many traditional Linux emulators[65].
VirtualBox
VirtualBox[66] is one of the most
popular Linux emulators that run on
Windows[67]. Thus, many Windows
admins have some prior experience with this platform. Since
VirtualBox runs easily on Linux, it is a good choice as a
virtualization platform.
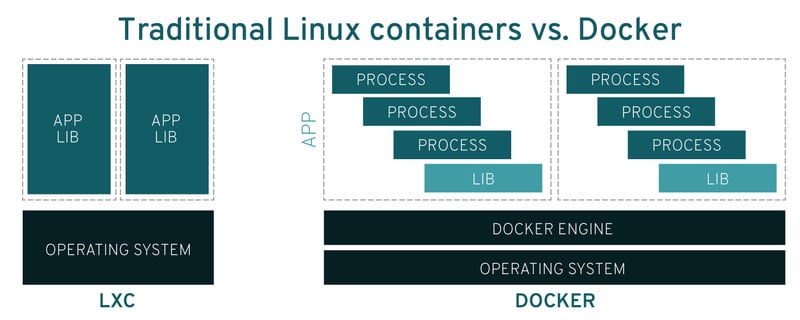
Docker
Docker[68] is a containerization
technology that offers application-level virtualization with high
scalability and quick deployment. This makes it a good choice for
powering cloud-native apps. Thus, many tech corporations who use
Linux for business use docker for deploying their cloud
services.
LXC and LXD
Linux
containers or LXC[69] is another
virtualization platform that works without the need for any
hypervisor. This makes it very CPU efficient and thus results in a
much better performance. Moreover, LXC containers offer more
isolation than Docker. LXD is a daemon for creating and managing
LXC containers more effectively.
ownCloud
ownCloud is a collection of client-server software that allows
users to build personalized cloud servers for home or office usage.
It is a community-driven project but also offers many excellent
enterprise offerings.
Seafile
Seafile is another powerful file-sharing software that can be
used for building your own cloud. All files are hosted on the
central server component, and individual machines can access them
using apps or a web interface.
10. Science and
Education
Linux offers many powerful and feature-rich educational
software, including tools for Physics, Biology, Mathematics, and
even Astrology. We are outlining some tools that can be useful to
educational institutes who use Linux for business.
ROOT
ROOT is an object-oriented programming library developed by CERN
and facilitates the solving of high energy physics. It can also
solve problems related to astronomy and data mining.

OpenFOAM
OpenFOAM is a robust Physics tool for
Linux[70] that can be used for
solving problems related to continuum mechanics and computational
fluid dynamics. Since OpenFOAM is written in C++, it offers
excellent performance. The software also comes under GPL and is
thus free to use and modify.
Elmer
Elmer is a free simulation tool that allows us to create
multi-physical simulations for the mechanics of fluid matters,
solid structures, heat transportation, and many more. It comes with
many numerical problem-solving methods and is quite efficient for
problems related to Physics.
EMBOSS
EMBOSS is a tool for performing sequential analysis in the field
of biology and bioinformatics. It can crawl and retrieve sequential
data from the internet very quickly and can perform pattern
matching, string manipulation, and database indexing, among other
things.
NAMD
NAMD or Nanoscale Molecular Dynamics is a Linux
framework for simulating molecular dynamics[71]. It is written using
C++ and implements various parallelization techniques to offer
faster load times and overall performance.
Psi4
Psi4 is an open-source suite of programs for solving various
quantum chemistry problems. It is known for its high accuracy, fast
simulation, and efficient resource usage. Moreover, the software is
very easy to use and provides a robust Python API.
MPQC
MPQC is a popular Linux chemistry
tool[72] among academics and
graduates. It allows researchers to simulate the electronic
structure of molecules and periodic solids using the TiledArray
tensors library and the MADWorld runtime. It is freely available
for all POSIX-compliant systems, including Linux and BSD.
CaRMetal
CaRMetal is a free geometry software for Linux
distributions[73]. It is written using
the Java programming language and uses the C.a.R (Compass and
Ruler) engine. CaRMetal comes under the GNU GPL license and thus
provides permission for personalized modifications.
Geomview
Geomview is a lightweight but useful program for 3D
visualization. It allows us to work with Mathematica graphics
outputs and can project models in euclidean, hyperbolic, and
spherical plain.
Scilab
Scilab is an extremely powerful Linux package for numerical
computation. It implements a robust, high-level programming
language, which makes it very easy to solve real-world
computational challenges.
SageMath
SageMath is a feature-rich computer algebra system for Linux[74], which makes it easy to
tackle modern-day mathematical problems. It has a beautiful and
easy to use user interface and is built on top of popular
open-source packages like NumPy, SciPy, matplotlib, Maxima, and
R.
Ending Thoughts
You can choose from an abundance of essential tools and
technologies when you start using Linux for business ventures. Our
editors have compiled this guide with all the tools a company would
require when transitioning to Linux from a different platform. We
have covered tools that can be used by tech startups, academic
institutions, content creators, and even video editors. Hopefully,
we were able to provide you the insights you were looking for. This
guide should illustrate the fact that Linux is often more powerful
than many paid systems people use. Leave us a comment below if you
have any specific questions.
References
- ^
wide range of distributions
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Linux server distributions
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Everything You Need to Know About Linux
Ubuntu Server (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
best Linux desktop environments
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
gorgeous looking GUI
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
The 20
Best Xfce Themes for Linux System in 2020
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
our
guide on Linux email servers
(ubuntupit.com) - ^
open-source Linux email clients
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Mailspring
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Geary
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
instant messaging apps
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
clients for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
our earlier guide on Signal
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
solid video conferencing software for
Linux (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Linux productivity software
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
ClickUp
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
NATTT
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
useful time tracker app for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Medleytext
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Project Brainstorm
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
KeePassXC
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
password management tool for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
EncryptPad
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
sharing desktop sessions
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
GIMP
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Inkscape
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
editing vector graphics
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Krita
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
medical imaging software for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
an alternative to tools like Adobe
Lightroom (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
video editing software for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Linux
and BSD distributions (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
best electronic design automation
tools for Linux (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
FreeCAD
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
alternative to commercial CAD
applications like AutoCAD
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
services that will come in handy for
content creation (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
LibreOffice
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
FreeOffice
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Joomla
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
popular forum management solution
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
RedNotebook
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
The 20
Best Open Source BI Tools and Software in 2020
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
solid finance app for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
make sense of content to economic
relationships (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
great CRM solution for companies
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
prominent help desk software
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Apache web server
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Nginx
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
How to
Install OpenVPN in Ubuntu Linux: A Tutorial for Newbie
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
popular database management system for
Linux (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
PostgreSQL
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
essential Linux iptables rules
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
UFW
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
powerful security framework
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
essential Nmap commands
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Kali Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
monitoring tool for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
essential Linux backup solutions
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
our review of the Bacula Enterprise
solution (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Linux file system
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
best disk cloning software for Linux
distributions (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
GParted
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
partition manager for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
NAS (Network Attached Storage)
solution for Linux (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
traditional Linux emulators
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
VirtualBox
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
popular Linux emulators that run on
Windows (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Docker
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Linux containers or LXC
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
robust Physics tool for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Linux framework for simulating
molecular dynamics (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
popular Linux chemistry tool
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
geometry software for Linux
distributions (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
computer algebra system for Linux
(www.ubuntupit.com)
Read more https://www.ubuntupit.com/linux-for-business-grow-your-enterprise-with-these-applications/