A threat actor associated with the LockBit 3.0
ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation has been observed abusing
the Windows Defender command-line tool to decrypt and load Cobalt
Strike payloads.
According to a report published by SentinelOne last week, the
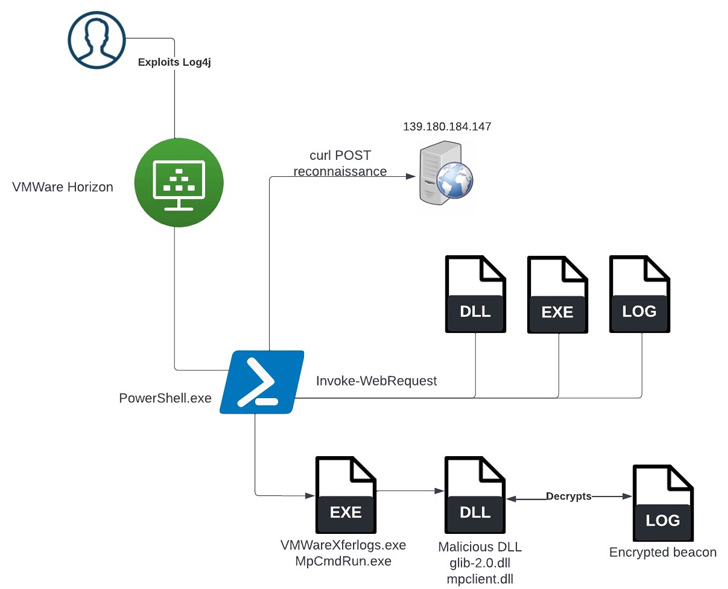
incident occurred after obtaining initial access via the Log4Shell vulnerability[1]
against an unpatched VMware Horizon Server.
“Once initial access had been achieved, the threat actors
performed a series of enumeration commands and attempted to run
multiple post-exploitation tools, including Meterpreter, PowerShell
Empire, and a new way to side-load Cobalt Strike,” researchers
Julio Dantas, James Haughom, and Julien Reisdorffer said[2].
LockBit 3.0 (aka LockBit Black), which comes with the tagline
“Make Ransomware Great Again!,” is the next iteration[3]
of the prolific LockBit RaaS family[4]
that emerged in June 2022 to iron out critical weaknesses[5]
discovered in its predecessor.
It’s notable for instituting what’s the first-ever bug bounty
for a RaaS program. Besides featuring a revamped leak site to
name-and-shame non-compliant targets and publish extracted data, it
also includes a new search tool to make it easier to find specific
victim data.
The use of living-off-the-land (LotL[6]) techniques[7]
by cyber intruders, wherein legitimate software and functions
available in the system are used for post-exploitation, is not new
and is usually seen as an attempt to evade detection by security
software.
Earlier this April, a LockBit affiliate was found to have
leveraged[8]
a VMware command-line utility called VMwareXferlogs.exe to drop
Cobalt Strike. What’s different this time around is the use of
MpCmdRun.exe to achieve the same goal.
MpCmdRun.exe is a command-line tool[9]
for carrying out various functions in Microsoft Defender Antivirus,
including scanning for malicious software, collecting diagnostic
data, and restoring the service to a previous version, among
others.
In the incident analyzed by SentinelOne, the initial access was
followed by downloading a Cobalt Strike payload from a remote
server, which was subsequently decrypted and loaded using the
Windows Defender utility.
“Tools that should receive careful scrutiny are any that either
the organization or the organization’s security software have made
exceptions for,” the researchers said.
“Products like VMware and Windows Defender have a high
prevalence in the enterprise and a high utility to threat actors if
they are allowed to operate outside of the installed security
controls.”
The findings come as initial access brokers (IABs) are actively
selling access to company networks, including managed service
providers (MSPs), to fellow threat actors for profit, in turn
offering a way to compromise downstream customers.
In May 2022, cybersecurity authorities from Australia, Canada,
New Zealand, the U.K., and the U.S. warned of attacks[10] weaponizing vulnerable
managed service providers (MSPs) as an “initial access vector to
multiple victim networks, with globally cascading effects.”
“MSPs remain an attractive supply chain target for attackers,
particularly IABs,” Huntress researcher Harlan Carvey said[11], urging companies to
secure their networks and implement multi-factor authentication
(MFA).
References
- ^
Log4Shell vulnerability
(thehackernews.com) - ^
said
(www.sentinelone.com) - ^
next
iteration (thehackernews.com) - ^
LockBit
RaaS family (www.sentinelone.com) - ^
critical
weaknesses (techcommunity.microsoft.com) - ^
LotL
(thehackernews.com) - ^
techniques
(thehackernews.com) - ^
leveraged
(www.sentinelone.com) - ^
command-line tool
(docs.microsoft.com) - ^
warned
of attacks (thehackernews.com) - ^
said
(www.huntress.com)
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/08/lockbit-ransomware-abuses-windows.html