As many as 47,337 malicious plugins have been uncovered on
24,931 unique websites, out of which 3,685 plugins were sold on
legitimate marketplaces, netting the attackers $41,500 in illegal
revenues.
The findings come from a new tool called YODA[1] that aims to detect
rogue WordPress plugins and track down their origin, according to
an 8-year-long study conducted by a group of researchers from the
Georgia Institute of Technology.
“Attackers impersonated benign plugin authors and spread malware
by distributing pirated plugins,” the researchers said[2]
in a new paper titled “Mistrust Plugins You Must.”
“The number of malicious plugins on websites has steadily
increased over the years, and malicious activity peaked in March
2020. Shockingly, 94% of the malicious plugins installed over those
8 years are still active today.”
The large-scale research entailed analyzing WordPress plugins
installed in 410,122 unique web servers dating all the way back to
2012, finding that plugins that cost a total of $834,000 were
infected post-deployment by threat actors.
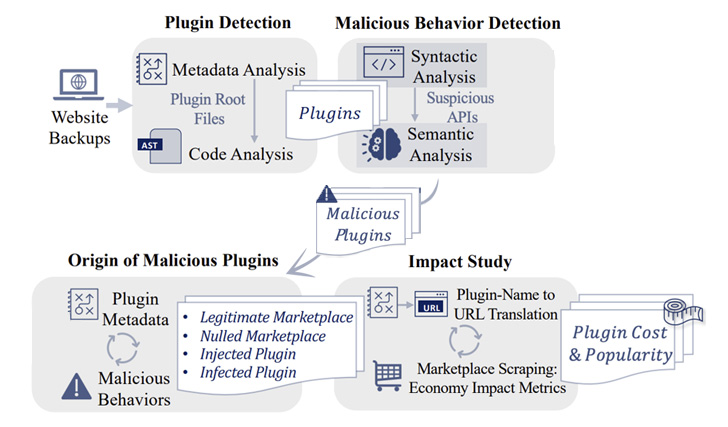
YODA can be integrated directly into a website and a web server
hosting provider, or deployed by a plugin marketplace. In addition
to detecting hidden and malware-rigged add-ons, the framework can
also be used to identify a plugin’s provenance and its
ownership.
It achieves this by performing an analysis of the server-side
code files and the associated metadata (e.g., comments) to detect
the plugins, followed by carrying out a syntactic and semantic
analysis to flag malicious behavior.
The semantic model accounts for a wide range of red flags,
including web shell, function to insert new posts,
password-protected execution of injected code, spam, code
obfuscation, blackout SEO, malware downloader, malvertising, and
cryptocurrency miners.
Some of the noteworthy findings are as follows –
- 3,452 plugins available in legitimate plugin marketplaces
facilitated spam injection - 40,533 plugins were infected post-deployment across 18,034
websites - Nulled plugins — WordPress plugins or themes that have been
tampered to download malicious code on the servers — accounted for
8,525 of the total malicious add-ons, with roughly 75% of the
pirated plugins cheating developers out of $228,000 in
revenues
“Using YODA, website owners and hosting providers can identify
malicious plugins on the web server; plugin developers and
marketplaces can vet their plugins before distribution,” the
researchers pointed out.
Read more https://thehackernews.com/2022/06/yoda-tool-found-47000-malicious.html